Strict competition requirements in the field of modern construction force us to look for ways to reduce costs, including the use of new materials. New formulations of building stone, special grades of concrete, foundation compositions, facing and thermal insulation materials. At the same time, in a market previously traditional for metal reinforcement and special structures, manufacturers of various composite products are actively trying to win their “place in the sun.” Most often these are non-metallic strength elements and fiberglass reinforcement.
Why did fiberglass reinforcement appear on the construction market?
Composite materials, including fiberglass reinforcement, are manufactured using a relatively simple technological principle of impregnating glass or basalt fibers with epoxy or polyester resin matrices. Next, the bundle is formed on a machine into a rod of composite reinforcement calibrated in diameter, and baked at a low temperature in a special drying oven. Typically, the length of one piece of reinforcement does not exceed 100 m.
Fiberglass reinforcement does not require the operation of complex and expensive equipment, so the production costs themselves are relatively low, most of the cost is the price of the resin for the matrix and the fiberglass tow. And yet, if you compare the cost of fiberglass and steel rods of the same diameter, metal reinforcement has a warehouse price that is 10-20% less, and this is a very big difference for such an area as construction.
Nevertheless, fiberglass material has quite strongly replaced rolled metal products, not least because of a number of specific properties, but the main factors were slightly different reasons:
- Fiberglass reinforcement has increasingly begun to be used in private low-rise construction. It is more accessible to use, it is easier and much cheaper to transport, store, and cut. It does not need to be straightened and leveled before use, as is the case with steel version. The material can be bought in a whole bay and cut into pieces of the most non-standard length. Whereas a standard 11-meter steel rod would require a lot of waste if your foundation, for example, has reinforcement 8 m long;
- The availability of equipment for the production of reinforcing strands has allowed many small enterprises - manufacturers of building materials - to establish continuous production of fiberglass reinforcement in the most various options performance of the rod surface. A huge number of offers, a competent sales policy and hidden advertising allow you to diversify the market;
- The desire of contractors to save money construction work on a more advantageous material for reinforcement, for which a formal, “blind” recalculation of the equivalent strength is often used composite materials And steel reinforcement.
Reviews from experts, advantages and disadvantages of composite thread
If you wish, you can find the most complex calculations and quite simple primitive arguments about why fiberglass reinforcement is good or bad. As a rule, serious research and reviews from specialists in most cases do not give specific recommendations, in fact, the “hot” problem of the foundation; in many ways, the capabilities of fiberglass-based reinforcement must be assessed at your own peril and risk.

Attention! Among the numerous reviews of specialists, there are practically no real professional experts in the field of structural mechanics of composite materials. Their opinion and feedback, as a rule, are reflected in the assessments and custom calculations of specific construction projects, cost a lot of money and are not presented to the public.
An approach can be called professional if the reviews of certain experts are evaluated specific situation using, for example, fiberglass rods in the foundation of a house using practical results and analyzing the reasons. Otherwise, you can name such expert reviews in best case scenario advertising or anti-advertising.
Using fiberglass rods in the foundation
Application reinforcing mesh based on fiberglass power elements began in the 60s of the last century. In addition, a fairly large number of buildings and technological structures made of stone and concrete have been built and are in operation, in the foundations and walls of which fiberglass-based reinforcement is used. Feedback on the condition of buildings with elements of steel and fiberglass reinforcement and many years of operating experience will give more than all the theoretical calculations of “experts” combined.
Almost everyone who makes videos or posts their opinion about the shortcomings of fiberglass reinforcement is either sales managers of competing steel products, or amateurs who confuse the causes and consequences of the basic principles of strength and rigidity of structures. For the most part, such discussions about the disadvantages of fiberglass reinforcement are accompanied by formulas and data on the strength of steel and composites. But there are no clear reasons or processes why fiberglass reinforcement cannot be used. If a person who undertakes to comment on the advantages and disadvantages of fiberglass reinforcement has not demonstrated in practice a fragment of destroyed concrete or a piece of foundation with fiberglass reinforcement, all his reasoning remains fantasies on an arbitrary topic.

Fiberglass reinforcement has been used in construction, mechanical engineering, and special projects for more than 40 years. If this issue is of fundamental importance to you, refer to old Soviet textbooks from the 70s of the last century, magazines on construction topics; these sources reveal the physics and mechanics of foundation destruction processes and provide numerous examples of errors.
Possessing high specific strength, fiberglass reinforcement can work perfectly in the most difficult conditions, but at the same time it has a number of disadvantages that limit its use in construction:
- The fiberglass nature of composite reinforcement has almost zero ductility of the material. In human terms, a frame for a highly loaded foundation or walls made of such a rod will not be able to plastically adapt to the redistribution of load in a loaded concrete stone. As a result, in some places the building’s foundation will experience overload, which can cause cracks to appear;
- The fiberglass base takes tensile axial loads very well, but compressive loads much worse, and tolerates shear forces catastrophically poorly. This means that any transverse shearing force, of which there are many in “fresh” foundations due to sedimentary processes, will lead to destruction of the integrity of the reinforcement;
- Unfortunately, during the time that the concrete of the foundation gains strength, the fiberglass frame behaves somewhat differently, and precisely at this stage, therefore, each specific case in the arrangement of reinforcement requires a very careful and careful analysis.

Therefore, in those units where it is permissible to replace metal with a composite material, instead of a traditional eight-millimeter rod, a six-millimeter fiberglass reinforcement strand can be used. Few people know, but today building slabs from stressed concrete with fiberglass reinforcement are already being produced. But in production such material is much more expensive, so almost 90% of the range, including for foundations, are custom-made products.
Application options for glass reinforcement
An undeniable advantage of steel reinforcement is the very well predictable behavior of the metal under the most difficult loading conditions. All existing skyscrapers and high-rise buildings are built only on steel reinforcement; moreover, most of these “wonders of the world” have an internal metal frame.
Glass fittings for high-rise buildings or highly loaded foundations will not be suitable. The structural mechanics of foundations is, in general, a whole science, primarily due to the complex interaction of individual parts of the foundation with the soil, with the walls of the entire structure.
IN existing model The most problematic areas of the foundation are the corner zones, where the reinforcement experiences tensile, bending and shearing loads. In these places, not every steel reinforcement is able to provide a rigid connection of corner blocks. The metal reinforcement in the foundation block achieves this only due to a combination of high ductility and elasticity. Fiberglass reinforcement cannot be used in these foundation units. Despite its high longitudinal strength, it will not be able to withstand twisting and cutting at the corner contact point of the foundation.
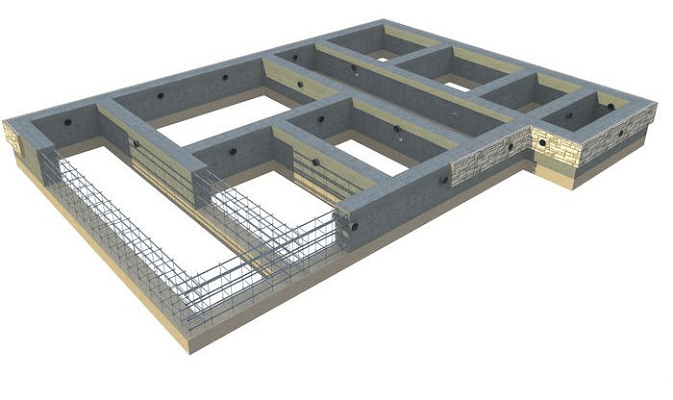
The strength and ductility of fiberglass reinforcement will be sufficient to build a foundation and basement one or two-story house. But provided that in the corner joints of the foundation, special couplings will be used to splice the reinforcement at right angles. Moreover, fiberglass is easy and simple to use for simple strip foundation 70-90 cm deep.
The use of fiberglass reinforcement in combination with special grades of concrete for the foundation is considered successful. Often, when special additives are used in the foundation to enhance frost resistance or water resistance, steel reinforcement begins to corrode intensively. Especially in foundations on soils with a high salt content or in close proximity to transformer substations.
Within the walls low-rise buildings, especially from aerated concrete block, arbolite stone and any other building material with low rigidity and contact strength, the use of fiberglass reinforcement is even encouraged. It is much simpler and easier to work with than a steel bar.

In addition, composite reinforcement is simply ideal for attaching external insulation or masonry facing bricks, where either galvanization or stainless steel is required. And, even more so, it is worth using a thin glass thread for working on the base blocks of the foundation.
Conclusion
Another problem characteristic of Russian reality, which is definitely worth mentioning. This is the low quality of the fiberglass reinforcement of the domestic manufacturer. Almost every coil with reinforcement has fracture defects.

During storage and transportation, a metal rod can be stolen or barbarically unloaded in an inconvenient place far from the foundation. But in any case, its quality will not suffer. Fiberglass thread can be easily damaged during transportation and not even notice it. It is definitely impossible to lay such reinforcement in the foundation.
Fiberglass reinforcement is widely used in construction in the West, while its use in the domestic industry is not widespread. However, recently the popularity of this material is growing, the reason for this is the many operational advantages compared to traditional rolled metal.
This article presents fiberglass reinforcement (FRP). We'll consider specifications, advantages and disadvantages, standard sizes and use of composite reinforcement.
1 Assortment and GOST standards
Non-metallic composite reinforcement was developed back in the USSR in the 60s, however mass production The material was never established due to the high cost of fiberglass at that time. However, composite reinforcement was used in the construction of several large objects, including power lines in Batumi, Moscow and bridges in Khabarovsk.
To date, there is no GOST standard with technical requirements for this material (the project is under development). Main normative act is SNiP No. 52-01-2003 "Composite reinforcement", according to which fiberglass products can be used in construction as a replacement for rolled metal. Each manufacturer has specifications for its products, along with which test reports and approval certificates are supplied.

Composite reinforcement is produced in the diameter range of 4-20 mm. The profile of the rods can be corrugated or smooth. Depending on the material of manufacture, the following types are distinguished: metal products:
- ASP - fiberglass reinforcement, made from fiberglass bound with a layer of synthetic resin;
- ABP - basalt-plastic products, in which the fiberglass core is replaced by a melt of basalt fibers;
- ASPET - products made of fiberglass and polymer thermoplastic;
- AUP - carbon fiber reinforcement.
The most common in construction are ASP and ABP; carbon fiber reinforcement is used less frequently due to lower mechanical strength material.
1.1 Areas of application
Application of sp. reinforcement in construction is practiced in the construction of residential, public and industrial buildings, as well as low-rise buildings, where ASP is used for:
- reinforcement iron concrete structures(walls and floor slabs);
- repair of surfaces of brick and reinforced concrete objects;
- layer-by-layer masonry of walls using flexible connection technology;
- all types (slab, strip, column);
- strengthening walls and aerated concrete blocks and installing monolithic reinforced belts.

The use of sp. is widespread. fittings and in the field of road and railway construction, in which ASP is used:
- when constructing embankments and road surfaces;
- when strengthening road slopes;
- during the construction of bridges;
- when strengthening coastlines.
Composite polymer reinforcement for reinforcing concrete structures is completely resistant to corrosion and chemically aggressive substances, which significantly expands the scope of its application.
1.2 Advantages of TSA
Composite reinforcement has the following operational advantages:

Disadvantages of s.p. reinforcement - low modulus of elasticity (4 times less than that of steel), which limits the possibility of its use in vertical reinforcement, and a tendency to lose strength when heated above 600 degrees. Please note that composite The reinforcement is not subject to bending under conditions construction site
— if it is necessary to use bent elements, they must be ordered separately from the manufacturer.
2 Comparison of ASP and metal analogues
We bring to your attention a comparison of the technical characteristics of composite and steel reinforcement.
| Type of fittings | Metal | Fiberglass (FRP) |
| Material of manufacture | Steel grade 25G2S or 35 GS | Fiberglass bonded with synthetic resin |
| Weight | 7.9 kg/m 3 | 1.9 kg/m 3 |
| 360 | 1200 | |
| Modulus of elasticity (MPa) | 200 000 | 55 000 |
| Relative extension (%) | 24 | 2.3 |
| Stress-strain relationship | Curved line with yield plateau | Straight line with elastic-linear dependence until destruction |
| Linear expansion (mm/m) | 14-15 | 9-11 |
| Resistance to corrosive environments | Low, susceptible to rust | High, does not rust |
| Thermal conductivity of materials (W/mK) | 47 | 0.46 |
| Electrical conductivity | Present | Dielectric |
| Diameters | 6-80 mm | 4-20 mm |
| Measured length | 6-12 m | Arbitrary length according to customer's request |
Let's consider a comparison of interchangeable diameters of composite and metal products using the example of rods:
- A3 6 mm - ASP 4 mm;
- A3 8 mm - ASP 6 mm;
- A3 10 mm - ASP 8 mm;
- A3 12 mm - ASP 8 mm;
- A3 14 mm - ASP 10 mm;
- A3 16 mm - ASP 12 mm.
2.1 Overview of fiberglass reinforcement (video)
3 Technology for the production of composite products
Fiberglass reinforcement is made from roving (fibers of the original raw material), a binder material - polymer resin, a hardener and a hardening accelerator. The specific ratio of materials depends on the temperature and humidity inside the production room.
Read also: what is the difference between reinforcement and what are its parameters?
The production line includes the following equipment:
- Heating hopper - this is where the fibers are heated to increase adhesion to the resin.
- Impregnation bath - the roving is impregnated with a mixture of resin and hardeners.
- Wrapper - presses raw materials through dies, through which rods of a given diameter are formed.
- Equipment for applying sand, where sand granules are evenly distributed over the surface of the rod, and excess is removed by air flow.
- A polymerization furnace, where the rods gain their design strength.
- Equipment for cooling products is a 3-5 meter long line located at the outlet of the polymerization oven.
- Broaching equipment, cutting mechanism and installation for winding coils - finished fiberglass reinforcement is cut into sections of the required length or wound into commercial coils 50-100 m long.

There are many on the market standard solutions, including all necessary equipment. The cost of a new line varies between 3-5 million rubles.
Medium productivity equipment is capable of producing up to 15,000 m of reinforcement during a working day.
Composite reinforcement is not a new material, but today it is actively expanding the boundaries of application, thanks to economical production technologies polymer materials. This modern alternative to steel reinforcing bars and wire differs from its metal counterparts in its raw material base, technical properties And appearance. Produced in accordance with GOST 31938-2012 and technical specifications manufacturers.
Main components of polymer composite reinforcement
The composition of these products includes two or more materials - the main one (matrix) and fillers, including reinforcing ones. The matrix and filler are selected in such a way that they form an overall structure that provides optimal performance characteristics for a specific purpose.
Matrix
It is a cured thermosetting resin that provides stress transfer and distribution in the reinforcing filler. The resistance of products to moisture, fire, and chemical environments depends on this structural component. Thermosetting resin - polyester, epoxy, vinyl ester, phenolic - after curing, is a solid material with a three-dimensional network structure.
Reinforcing fillers They are fibers - continuous or staple, which depends on the manufacturing method. Depending on the raw materials used, fibers are distinguished:- Glass- made of inorganic glass.
- Basalt- produced from basalt and gabrodiabase.
- Carbon- are formed by pyrolysis of organic precursor fibers - polyacrylonitrile or cellulose hydrate. According to the elastic modulus and tensile strength, carbon reinforcing fillers are divided into - general purpose, high-strength, medium-, high-, ultra-high modulus.
- Aramid. The feedstock is linear fiber-forming polyamides.
- Combined composites include reinforcing fillers from two or more raw materials. For example, ASPET rods contain glass fibers and thermoplastic polymer fibers.

- ASK (ASP)- glass composite, the advantages of the material are a combination of low weight, high strength and affordable cost;
- ABK (ABP)- basalt-composite;
- AUK (AUP)- carbon composite, has good strength, but due to its high cost its use is limited;
- AAK (AAP)- aramidocomposite;
- ACC- combined. In this series, products made on the basis of glass and basalt fibers are widely used due to the combination of good wear resistance and reasonable cost.
Table of main characteristics various types composite reinforcement
Design features
Manufactured with a periodic profile. The product design includes:

- Power rod- a solid element on which the main technical characteristics of the product depend.
- Anchoring layer. It is located evenly, at an angle to the longitudinal axis. It is formed by winding fibers around a power rod. Improves the adhesion of polymer reinforcement to hardening concrete mixture.
Periodic profile reinforcement is characterized by the following parameters:
- Outside diameter. Measured at the tops of periodic protrusions.
- Nominal diameter. This value is indicated in the product labeling and is used in structural calculations.
- Periodic profile pitch. The distance between the centers of adjacent protrusions is determined parallel to the vertical axis of the rod.
Positive and negative characteristics of polymer composite reinforcement
This type of reinforcement cannot yet act as a full replacement for steel reinforcing rods. However, there are areas of application in which the use of composite reinforcement is more rational, due to a set of advantages, including:- Chemical passivity. Due to this property, polymer products can be used under exposure conditions sea water, alkaline and acidic environments, road chemicals.
- Cutting speed in size under construction site conditions is significantly higher compared to cutting steel rods.
- Low thermal conductivity. Polymer reinforcement increases thermal insulation characteristics design, due to the absence of cold bridges.
- Low temperature resistance.
- Light weight. Facilitates the transportation of products, warehousing, and installation work.
- Lack of current conductivity, magnetoinertness and radio transparency. This quality ensures the demand for polymer products in the construction of laboratories and other facilities for which the shielding factor is important electromagnetic waves. In structures that use polymer reinforcement, there are no stray currents.
Characteristics that limit the scope of application of composite reinforcement:

- Inability to bend rods at a small angle at the installation site. If there is such a need, then the production of bent products is ordered at production sites.
- Low modulus of elasticity, limiting the use in vertical reinforcing structures.
- No possibility of welding frames. Flat and three-dimensional structures from polymer rods are constructed only by tying and using plastic clips.
- Low resistance to high temperatures . Therefore, use such products in structures that are exposed to heat, or in objects with high fire hazard Not recommended.
- Aging. Like all polymers, composite reinforcement loses its characteristics over time. Although manufacturers claim that its operational period is at least 80 years.
Areas of use
This building material is most effective in areas where the use of metal reinforcement is undesirable or impossible. Polymer reinforcing rods are used for:
- installation of foundations for buildings operated in aggressive environments;
- strengthening foundations or load-bearing walls;
- strengthening the road surface, embankments;
- strengthening soils in mines;
- formwork devices for large tanks;
- strengthening floor screeds;
- shoreline strengthening;
- production of flexible connections between structural elements of buildings, for example between outer wall and finishing facade material.
Attention! The use of composite reinforcement in floor slabs, lintels and others structural elements working in tension is not recommended due to the high flexibility of the material.
Comparison of properties of polymer composite and steel reinforcement
Table comparing the characteristics of fiberglass and steel reinforcement
| Low alloy steel 25G2S or 35GS | Inorganic glass melt fibers, thermosetting resins and other additives |
| Density, kg/m 3 | 7900 1900|
| Tensile strength, MPa | 360 800|
| Modulus of elasticity, GPa | 200 55|
| Relative extension, % | 242,3 |
| Resistance to chemically aggressive environments | Subject to corrosion, to increase anti-corrosion characteristics it is required protective covering, for example zinc | High stability, no anti-corrosion measures required
| Electrical conductivity | HighAbsent |
| Thermal conductivity, W/mK | 47 0,46
An argument in favor of replacing steel reinforcement with polymer reinforcement is the possibility of using a polymer product with a smaller diameter compared to metal, based on standard values of tensile strength. By Order of the Ministry of Construction and Housing and Public Utilities of the Russian Federation No. 493 dated July 08, 2015, Appendix L established reduction factors for standard tensile strength, taking into account actual operating conditions.
Table of reduction factors to the standard values of tensile strength presented in GOST 31938-2012
This table means that if polymer composite reinforcement, for example fiberglass (FRP), is designed to operate under long-term indoor loads, then the calculated value of tensile resistance is found by the formula:
R calculated = R normal * 0.8 * 0.3 = 800 * 0.8 * 0.3 = 192 MPa

Therefore, when choosing the diameter of polymer reinforcement, which should replace steel, you should not use the standard values of tensile strength presented in GOST, but calculated in accordance with real operating conditions.
In connection with the factors stated above, we can conclude that composite reinforcing rods are a promising building material. However, it is only effective in certain applications and it is recommended that you consult with qualified professionals before using it.
GD Star Rating
a WordPress rating system
The construction industry is one of the fastest growing and changing in the world. modern world. Before one has time to appear somewhere in the depths of a specialized university, the idea is immediately picked up by business. Fiberglass reinforcement is one of these materials that has literally revolutionized the construction industry. Successful combination science and engineering made it possible to create a special material for construction and installation work, which bypasses traditional ones in quality and characteristics.
Key role in the composition building material are played by special fiberglass fibers that are impregnated with a special polymer composition. The material is produced in the form of rods with a diameter of 4 to 18 mm. The length can reach 12 meters. The main “feature” of the material is its multi-layer nature and special polymer “impregnation”.
For your information! Fiberglass fittings are usually supplied in the form of twisted coils; in appearance they resemble a large coil of dense cord or wire. However, if the diameter of the product is more than 10 mm, it is sold only in rods.
In the literature and GOST, two abbreviations are mentioned, indicating the same material: SPA or ASP. Both abbreviations are equivalent.

The rod consists of two layers:
- 1st layer – inner core. It is based on fiberglass fibers arranged strictly parallel to each other (it is no coincidence that we compared the reinforcement with a rigid wire), or in the form of a “pigtail”. These threads are thin, but surprisingly strong; they are soldered to each other with a special polymer composition. It is these fibers that provide the main characteristics of the product.
- 2nd layer – outer. The “shell” can be a fine abrasive, specially sprayed, or fibers, this is the so-called reinforcing winding.

The main characteristics for this material are most often called:
- diameter – this indicator affects the calculation of the product’s bending and tensile strength;
- weight. By the way, this indicator distinguishes fiberglass from other products, in particular metal fittings;
- winding step. The characteristic is relevant for ASP with a relief coating.
Interesting fact! Fiberglass is 9 times lighter than metal rods.
Areas of application and types of fiberglass reinforcement
The use of fiberglass reinforcement is quite widespread. Due to the possibility of using not only rods, but also reinforcing mesh, it is used in construction and construction of various, sometimes very complex, geometries. Moreover, the sizes of finished structures can be very different.

In addition, fiberglass reinforcement can be used in:
- road construction and pavement reinforcement;
- strengthening masonry and other block-type building materials;
- reinforcement and;
- strengthening and fencing structures poured.
Advice! In dacha farming, fiberglass reinforcement is useful in the construction of outbuildings, enclosures, as well as greenhouses and greenhouses. It can be used as support structures for gartering plants, as a basis for decorative trellises.
Options for using spas in construction and gardening.



Production and requirements for fiberglass reinforcement
Like any technically complex production, the creation of high-strength reinforcement is a labor-intensive and expensive process. It is necessary to use high-precision equipment to create a special mixture.

All the main elements of the SPA production line are shown in the diagram:

Pros and cons of composite fiberglass reinforcement
Fiberglass reinforcement is considered the most promising material used in the construction of reinforcing structures and frames. Among the advantages are:
- high resistance to corrosion;
- low thermal conductivity;
- durability;
- light weight;
- 3.5 times stronger than metal;
- versatility;
- tensile strength;
- does not conduct current;
- not afraid of frost;
- seamlessness;
- does not require welding.
Among the disadvantages:
- low elasticity,
- low thermal stability.
What to look for when choosing
Due to the large number of standard sizes, it is necessary to take into account the conditions of use and the load on the material. That is why, immediately when purchasing, pay attention to the following points:
- design option for the top layer and quality of winding of the reinforcing tape;
- diameter and absence of chips and damage on cuts;
- color. It should be uniform. The shade must match the description in the documentation;
- availability of documents of compliance with GOST.
When choosing a spa, it is best to initially find out the reputation of the manufacturing company of this material, for which you need to read reviews on the Internet and in other sources of information.
Which reinforcement is better: metal or fiberglass?
Perhaps, if we compare these two materials, the usual metal material significantly loses in quality, but wins in price. In this case, you should pay attention to the scope of application. And also study comparative characteristics.
| Characteristic | Metal | Fiberglass |
| Tensile strength, MPa | 390 | 1300 |
| Coefficient, W/m 2 ×K | 46 | 0,35 |
| Density, kg/m 3 | 7850 | 1900 |
| Elasticity | + | + |
| Plastic | + | - |
| Corrosion resistance | - | + |
| Dielectric properties | - | + |
Leading manufacturers
There are about 10 proven manufacturers of fiberglass reinforcement that have managed to prove themselves in this market segment. Moreover, enterprises exist in almost all major geographical areas: the central part of Russia, as well as Siberia and the Urals. Let's name the largest of them:
- NPC "Spetspolymer", NPC "ARMASTEK", Moscow Composite Materials Plant. (Moscow and Moscow Region);
- Leader-Composite (St. Petersburg and Leningrad region)
- "Yaroslavl Composites Plant";
- "Uralteplostroy", LLC "UZKT", LLC "Elpromtekh", LLC NPF "UralSpetsArmatura" (Ekaterinburg);
- "Volga region fittings" (Saratov).
Review of prices and user reviews of composite fiberglass reinforcement
The cost of the material is calculated based on the price for linear meter. The final cost is influenced by both the quality of the raw material, its composition and number of layers, as well as the diameter of the intended workpiece. Let's present the average data for September 2018 in rubles.
| Manufacturer | Brand | Diameter, mm | Outer layer type | Cost, rubles/p. meter |
| PC "Composite" | ASK | 8,0 | with coiling | 11,9 |
| 10,0 | 17,9 | |||
| 12,0 | 26,9 | |||
| TSA | 8,0 | with sand coating | 13,9 | |
| 10,0 | 23,9 | |||
| 12,0 | 38,9 | |||
| "ArmatSoyuz" | SPA | 4,0 | with coiling | 6,9 |
| 6,0 | 7,9 | |||
| 8,0 | 11,5 | |||
| 10,0 | 17,5 | |||
| 12,0 | 26,9 | |||
| 14,0 | 42,9 | |||
| 16,0 | 60,9 | |||
| 18,0 | 94,9 | |||
| "Armplast" | ASK | 4,0 | with coiling | 5,5 |
| 6,0 | 7,9 | |||
| 8,0 | 11,5 | |||
| 10,0 | 17,9 | |||
| 12,0 | 26,9 | |||
| 14,0 | 42,47 | |||
| 16,0 | 60,52 | |||
| 18,0 | 94,32 | |||
| 20,0 | 117,6 | |||
| 22,0 | 138,99 | |||
| 25,0 | 180,17 | |||
| 28,0 | 223,10 | |||
| 32,0 | 292,74 | |||
| 36,0 | 312,80 |
If we talk about the features of using the material and reviews about it, experts note the high quality of the material and its sufficient performance. Due to its high wear-resistant qualities, fiberglass reinforcement has gained its fans among both professional builders, and among home craftsmen.
However, there are those who are distrustful of the material.
Feedback on the use of fiberglass reinforcement:
More details on Drom.Forum: https://forums.drom.ru/house/t1151870250-p3.html
And if you have own opinion regarding the use of this material in construction, its advantages and disadvantages, share your opinion with other readers of the site.
From this article you will learn:
Let's try to figure this out and decide where the use of fiberglass reinforcement is justified and where it is not.
The fiberglass reinforcement itself is a fiberglass rod with a thread wound around it in the form of a spiral for good adhesion to concrete. Its use is justified in many cases, but in some designs its use is highly discouraged.
Now let's look at everything in order - first consider the advantages and disadvantages of fiberglass reinforcement, and then, based on them, determine where its use would be appropriate. At the end of the article I will tell you about my personal opinion about use of fiberglass reinforcement.
Like any building material, fiberglass reinforcement has its own advantages and disadvantages compared to similar metal ones, which can be a serious help or hindrance in its use in various areas of construction.
Let's probably start with the advantages:
Advantages of fiberglass reinforcement
1. Small specific gravity . This advantage allows it to be used in lightweight structures, such as cellular concrete and so on. This property of fiberglass reinforcement makes it possible to reduce the weight of the entire structure.
It is worth noting that the use of fiberglass reinforcement in ordinary concrete will not significantly affect the weight of the structure, given that the main weight will be provided by the concrete itself.
2. Low thermal conductivity. As is known, fiberglass conducts heat through itself much worse than metal.
This advantage of fiberglass reinforcement allows it to be used where it is necessary to reduce the cold bridges that steel reinforcement so wonderfully creates.
3. Packaging in coils. For the construction of private houses, this is a very significant advantage of fiberglass reinforcement, because you don’t have to spend money on its delivery to the site, and, as you know, when building a house, especially if you build it yourself, every penny counts.
In addition to the above, we can add that the use of fiberglass reinforcement in coils reduces its consumption, since there will be practically no overlaps in the reinforcement cage, and this will also slightly reduce financial costs.
 4. Durability. Manufacturers rely on the fact that fiberglass, compared to metal, is much more durable.
4. Durability. Manufacturers rely on the fact that fiberglass, compared to metal, is much more durable.
This is a slightly dubious advantage of fiberglass reinforcement, given that the metal inside concrete is practically not subject to corrosion and inside a reinforced concrete structure will also last a very long time.
5. Dielectric. This property, most likely, in private construction does not give any advantages to fiberglass reinforcement over metal, but it should not be forgotten either.
6. Resistant to chemical influences . This means that in acidic and other aggressive chemical environments, fiberglass reinforcement is much more comfortable than steel.
In low-rise private construction, this advantage of fiberglass, just like the previous one, plays practically no role, with the exception of construction in winter, when various salts are added to the mortar or concrete, which have a detrimental effect on the metal.
7. Radio transparency. This means that fiberglass reinforcement does not create any radio interference, unlike metal contours created by steel reinforcement.
Such an advantage of fiberglass reinforcement as radio transparency will play a significant role only if there is a lot of reinforcement in the walls of your house. Then the use of fiberglass reinforcement will reduce radio interference inside the house.
We've sorted out the advantages, now let's look at the disadvantages of fiberglass reinforcement used in construction.
Disadvantages of fiberglass reinforcement
Any material has disadvantages and fiberglass reinforcement is no exception.
1. Fiberglass reinforcement is more expensive ordinary steel when comparing reinforcement of the same diameter.
This is a slightly dubious drawback, since manufacturers claim that in construction, fiberglass reinforcement is used with a smaller diameter than metal reinforcement.

2. Thermally unstable. Fiberglass reinforcement does not withstand high temperatures.
It’s also a dubious drawback, because in low-rise private construction I can’t even imagine a situation where it would be necessary to heat the reinforcement to 200 degrees.
3. Doesn't bend. Thus, if we need, for example, to bend the reinforcement at an angle of 90 degrees, we will not be able to do this. Although, on the other hand, we can make all the bends from ordinary steel and extend them with fiberglass.
4. Low modulus of elasticity at fracture. This means that fiberglass reinforcement does not withstand the same loads as metal reinforcement.
Many manufacturers claim the opposite - that the modulus of elasticity of fiberglass reinforcement is greater, but this, most likely, they mean tensile, and concrete, as a rule, is subject to greater loads due to fracture. This is the main drawback due to which the use of fiberglass reinforcement in construction is limited.
5. Difficulty in constructing a rigid reinforcement frame. In other words, a frame made of fiberglass reinforcement is not as rigid as one made of metal, and, accordingly, is less resistant to vibration and loads that will be present when pouring concrete from a truck mixer.
When you pour concrete into a trench or formwork from an automixer, it is necessary that the reinforcement frame be very rigid, because the reinforcement can “jump off” or simply press against the floor or walls of the trench, and this will be difficult to correct once the concrete has already been poured.
So we have examined almost all the main advantages and disadvantages of fiberglass reinforcement. Judging by them, it is impossible to say with great confidence that it is significantly better or worse than metal fittings, so let's look at which building structures and structures, the use of fiberglass reinforcement will be justified and advisable.
Application of fiberglass reinforcement in construction
The use of fiberglass reinforcement is justified in some cases, both in industrial construction and in private low-rise construction.
Regarding industrial construction, I think there’s no point in saying much; after all, the site is dedicated to building houses with your own hands, so let’s look at the scope of application of fiberglass reinforcement in private low-rise construction.
1. Fiberglass reinforcement is used in some types of foundations, such as strip foundations - buried below the freezing depth, slab foundations.
It is worth noting that this applies only to low-rise private buildings, on good soil. On floating soils there will be increased fracture loads, which fiberglass reinforcement may not withstand.
2. It is advisable to use fiberglass reinforcement in reinforcement brick walls, walls made of blocks, very often you can find reinforcement of walls made of gas silicate blocks with fiberglass reinforcement.

The use of fiberglass reinforcement in wall reinforcement is very popular among developers. Moreover, such reinforcement is used both as an element of reinforcement of the walls themselves, and as a ligament facing wall with carrier.
3. In multilayer panels as connections. Since there is usually dense insulation inside the panels, fiberglass reinforcement is used to bind the concrete parts together.
4. The use of fiberglass reinforcement in load-bearing parts of elements subject to increased corrosion, for example, swimming pools, is justified.
Metal reinforcement will be subject to corrosion when concrete is in water, but fiberglass reinforcement does not have this disadvantage, based on one of its advantages.
5. Fiberglass reinforcement is also widely used in reinforcing laminated wooden beams, increasing their rigidity.
6. Asphalt reinforcement in areas of high loads, although I have never seen this before.
As you can see, the scope of application of fiberglass reinforcement in construction is quite wide, although there are some restrictions.
The author's opinion on the use of fiberglass reinforcement in construction
I believe that fiberglass reinforcement is not yet capable of completely replacing metal, but this does not mean that it can be completely neglected.
I widely use it in the construction of walls made of block and brick, also as connections between a facing wall and a load-bearing wall, since when using metal as connections, firstly, it will be susceptible to corrosion, and secondly, metal creates cold bridges, which in modern construction extremely undesirable.
The use of fiberglass reinforcement in the foundation is also justified if you have a light building, for example, frame house or garage.
If the site has weak soil and foreseeable huge loads on the foundation, I would not take risks with the use of reinforcement, whose elasticity to fracture is less than that of metal.





