In the bathhouse it is important to maintain optimal level humidity and temperature: steam, heat and the sharp temperature drop accompanying them have a destructive force that can even deform building materials newest generation. But how to make ventilation in a bathhouse so that such fundamental characteristics strengthen the durability of the entire building, and our health too? Let's consider the best options.
It has been proven that wood (the main material for building baths) will last up to 20 years in these harsh conditions, but only with intensive air exchange. And the constant insufficient flow of dry air will force us to replace the casing in the steam room within 5 years, paying a substantial amount for this repair.
Due to shortage fresh air wooden cladding is intensively affected by fungi and bacteria and depresses us with a persistent unpleasant odor. By the way, the use of aggressive disinfectant chemicals in a bathhouse is absolutely prohibited. Therefore, let’s figure out how to properly ventilate a bathhouse in order to completely remove this harmful “cocktail” from the room, reinforced by mold and mildew spores.
Ventilation in the bath

Ventilation is the process of removing exhaust air and complete replacement its external.
The mechanism of ventilation is simple: fresh air passes into the room through one hole, and through the second (exhaust) it goes outside. The strength of the air vortex depends on the size and location of such vents. Correct calculation of parameters for a specific bathhouse will help us avoid popular mistakes.
Features of ventilation
Let's look at how to properly ventilate a bathhouse.
Projects are carried out by professionals for any baths, but during installation it is important to comply with such conditions.
- directly during construction, since it is not easy and dangerous to punch holes for ventilation in already finished building. In addition, a suitable ventilation scheme will inevitably require corresponding changes in in general terms building.

- The exhaust hole is always larger than the supply vent: to speed up the outflow, 2 hoods are also installed. In this case, the exhaust air will leave the room faster, making room for fresh air.
- We will regulate the speed of such substitution using valves: we will close them completely when heating the bath in order to quickly reach the desired temperature. In addition, in winter we also cannot do without such containment of the natural cold flow. So, the valves perfectly regulate the intensity of ventilation.
- The cross-section of the hole is strictly proportional to the volume of a particular room: 24 mm per 1 cubic meter. m.

The photo shows a bolt on the hole.
- The supply ventilation system also involves heating the air in winter and cooling it in summer. Exhaust ventilation only removes unhealthy air from the steam room.
Note!
The exhaust vent cannot be placed opposite the supply vent: the air mass will not have time to gradually and gently mix, and a dangerous draft will form.
- A strong convection flow will freshen the air as much as possible, because in 1 hour almost 10-fold renewal of the atmosphere in the steam room is required.

Ventilation methods
Experts have developed optimal options for the location of the ventilation hatches themselves in the steam room, and the choice of a specific layout depends on the features of the construction of the bathhouse. Let's look at the most popular types.

Behind the stove
- The inlet hole will be very useful below the stove, while the heater will be in the path of fresh but cold air.
- We make exit channels directly in the floor, and the subfloor communicates with the one leading to the street.
- The exhaust air descends and goes underground through the holes, and from here escapes through the pipe.
- This scheme saves heat and drains the always damp underground, preventing the appearance of smelly and harmful mold spores there.

Above the stove
- The inlet for outside air is equipped above the heater, and the outlet is made in the opposite wall, but below the inlet.
- Then the warm flow near the stove will raise the cold one, then fall and go outside.
- Cold air will not be able to penetrate through the outlet duct.

Under the stove
- We make an inlet hole next to the stove, at the bottom.
- Cold air passing by the furnace heats up and goes up.
- We place the outlet pipes in the opposite corner, one a meter from the floor, the second under. They are connected by a single ventilation duct, which we lead into a common duct or onto the roof, or possibly into the attic.
- All openings are equipped with grilles and valves that regulate the intensity of air flow.

Stove draft
If the stove is built directly in the steam room, we will use this ingenious scheme:
- We arrange the heater so that the vent is below the floor, and we equip the inlet ventilation duct a little higher, above the floor.
- Now the draft will be provided by the stove itself, without fans.
- Exhaust air leaves through its pipe, and a low supply inlet will increase the efficiency of the heater.

Underfloor hood
- We arrange the supply inlet behind the stove, one and a half meters from the level of the heater, but we make the exhaust hole on the opposite wall 30 cm below the floor.
- We install a fan in the exhaust hole.
- The advantage of the scheme is the uniform heating of the incoming healing air: the cold flow instantly heats up from the stove, goes under the ceiling, and when cooled, rushes down to the exit.
- The lower the hood, the stronger the recoil from the stove.
Other options

- Scheme 1: a cold stream enters the steam room, heats up from the stove and is removed through the hood on the opposite wall. A fan mounted in the hood is used to pump air.
- Scheme 2: the instructions recommend that both the supply and exhaust openings be placed opposite the stove on the same wall; the entrance is 30 cm from the floor, and the exit is 30 cm from the ceiling. This is an excellent scheme if there is only one bathhouse at home outer wall, and only we use it for ventilation vents.
- Scheme 3: we install an inlet opening behind the stove, 30 cm from the floor. We will place the hood on the opposite wall, also 30 cm from the floor.
- Scheme 4: for baths with a continuous cycle: here the heater vent is also an exhaust hood, so with our own hands we will equip only one supply hole near the floor, directly opposite the brazier.
Mechanical ventilation
Let’s clarify how to make the ventilation ideal in a bathhouse: it is the electric heater that will ensure an intensive supply of fresh air through the ventilation.
Artificial steam injection using a steam generator is widely used in modern Russian baths. Similar ventilation in Turkish bath with a mandatory humidity of 100%. Mechanical exhaust here is done under a dome, but an air dehumidifier is inserted into the pipe, removing moisture into the sewer.
Advice!
In Russian baths, where steam is prepared manually, we will use traditional methods of ventilation: we will sew the bottom of the doors with a ventilation grill.

High-speed ventilation evenly warms up and comfortably refreshes the room. Special fans are made of heat-resistant glass polyamide and can withstand heating up to +130 degrees, consuming from 18 W. The protection class of such a device is IP-44 and higher.
Conclusion
Organization of soft, gentle, but fresh airflow in the steam room while maintaining a pleasant microclimate - in a special layout of the supply and exhaust openings, as well as specially arranged auxiliary equipment for them.
Ventilation depends on:
- direction and amount of warm air;
- lack of waste;
- economical fuel consumption.
Mechanical ventilation involves the use of software devices that control and independently maintain the specified parameters of temperature, humidity, and fresh air. But the cost of such an ideal is significant. However, the choice is ours.
Combined ventilation is based on the patterns of placement of vents, and the pressure difference is given to us by mechanical devices that extract air - fans. This is the best option for bath ventilation.
The video in this article will clearly demonstrate to us the process of creating an optimal air environment in a bathhouse.
Often to provide ventilation you can limit yourself to aeration. It is necessary to make holes with dampers, it is advisable to choose the recommended places so that the air circulation is soft and constantly maintained. If necessary, you can use forced air exchange systems.
Above the stove
Opening for outside air equipped above the heater. The output is made in the opposite wall; it should be lower than the input. The warm flow will rise as a stream of cold air and exit through the hole. Thanks to the constant release of warm air, cold air will not be able to enter through the outlet.
Behind the stove
The air inlet hole can be positioned at the bottom of the wall behind the stove. The stove will heat the incoming, cold air, so there will be no drafts or sudden temperature changes. Output channels can be built in the floor. They can pass through the underground, passing into a ventilation pipe that removes air to the street. The air outflow created according to this scheme allows you to save heat, helps reduce heating costs, and gives comfort to those in the bathhouse. The main advantage is additional heating of the subfloor. It dries well, so it does not grow mold and various fungi.
Under the stove
A hole is made next to the stove as low as possible. When cold air passes by the stove, it heats up, so it rises. Exit holes are made in the corner located opposite the stove. To create the first, you need to measure 1 meter from the floor, and the second is built under the ceiling. They are combined by a ventilation duct, which can be brought to the roof, for example, through the attic.
Underfloor hood
The hole for the supply draft must be equipped from the back of the oven. It should rise 1.5 m from the level of the heater. The hood is installed under the floor, at a distance of approximately 30 cm. A fan is mounted in the exhaust hole. All incoming air will be heated absolutely evenly. First, the air masses are heated from the furnace and rise upward. After cooling down, they rush down and go outside. To keep warm for longer for a long time, you need to make the exhaust hole as low as possible.
Other popular options
- If there is no other possibility, you can make an air inlet anywhere on the wall near the stove, and an outlet also in a free location, but in the opposite wall. To speed up air circulation, you can install a fan for the outlet.
- The location of the inlet and outlet openings is on one wall opposite the stove. The air will enter through something installed at a height of 30 cm from the floor, and exit through something installed 30 cm from the ceiling. This scheme is perfect for baths with only one external wall.
- The inlet opening is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the floor behind the stove, and the outlet is also at a height of 30 cm, but on the opposite side.
- Option for baths with a continuous cycle. The heater vent is used as an exhaust hood, so there is a need to equip only one hole for air flow. It should be placed opposite the fryer at its level.
One of the main elements of ventilation for the bathhouse there is a chimney. Warm air escapes better through the pipe than through ventilation holes. To freshen the air as quickly as possible, you need to open the chimney along with the equipped openings.
The temperature in the bathhouse should not be allowed to drop lower than outside. In this case, there is a risk of smoke in the room in which the stove is located, usually a steam room. The cooled air forms a plug; it can be released by opening all the dampers on the ventilation openings and connecting the chimney. Sometimes you have to use a special opening to dispose of ash.
Video about how to make ventilation in a bathhouse with your own hands.
DIY sauna steam room ventilation
 It is advisable to install a stove in the steam room. It provides the main ventilation system. Air from the steam room passes through the vent, so its circulation is already well ensured. The blower is used instead special device for hood. For maximum air flow the oven must be installed at a level lower than the finished floor. To start ventilation you only have to open it a little. front door or a window. Disadvantage this method ventilation is to maintain it only while the stove is burning. If the device is inoperative, the hood is completely suspended.
It is advisable to install a stove in the steam room. It provides the main ventilation system. Air from the steam room passes through the vent, so its circulation is already well ensured. The blower is used instead special device for hood. For maximum air flow the oven must be installed at a level lower than the finished floor. To start ventilation you only have to open it a little. front door or a window. Disadvantage this method ventilation is to maintain it only while the stove is burning. If the device is inoperative, the hood is completely suspended.
In addition to the heater, ventilation in the bathhouse is maintained additionally equipped with holes(see photo below). They must be closed with gates with bars. To regulate the air exchange in the steam room, simply open or close the shutters. After each parka, the room needs to be ventilated, so you should open the holes for a while. If this is not done, the air will remain humid, heavy, and there is also a risk of carbon monoxide poisoning due to its high content.

When the steam room is just heating up, the stove is heating up, you need to make sure that the holes are tightly closed. When the room is warm enough, they can be opened. To avoid formation reverse thrust It is necessary to ensure at the construction stage that the area of the exhaust openings exceeds the supply openings. Steam accumulates at the very top, to lower it, you can spray water on the floor in small quantities. To quickly release steam, you can also wave a broom or towel in different directions.
If the stove is not installed directly in the steam room, then another ventilation technique is used. Near heating device make an inlet hole at a height of 30 cm from the floor. An exhaust hood is made on the opposite wall, positioning it 30 cm down from the ceiling.
Sometimes the inlet is placed behind the stove at the bottom of the wall. The air coming from the street is warmed by the stove, so the room cools down moderately. On the wall opposite to the stove you need to form 2 openings. They will form one exhaust duct. The first opening is made at a distance of 1 m from the floor, and the second under the ceiling. The air is discharged through the hood to the roof.
When installing such ventilation, the steam room quickly warms up, while saving fuel. The occurrence of a musty smell in the room is prevented, since the subfloor is well dried.

Natural ventilation
To bring fresh air into the bathhouse, you need to make a small opening in the wall, located at a distance of about 50 cm from the stove. It is equipped with a retractable damper, which allows you to regulate the amount of incoming air. Too much high location not reasonable, since the hottest air rises to the ceiling. To make the most of the heat from the stove, you need to make a hole in the middle of the wall. If the hole is too low, the draft will be minimal. In order for it to be carried out correctly, it is necessary to install a ventilation pipe or purchase a fan.
Forced ventilation
 To ensure that as much fresh air as possible enters the steam room, openings should be positioned diametrically to each other. If forced air outflow will be used, it is advisable to make the supply hole higher than the exhaust hole. If it is possible to construct a ventilation system in which the air flow comes from below, heats up from the stove, rises up, and then goes outside, then installing additional fans will not be necessary.
To ensure that as much fresh air as possible enters the steam room, openings should be positioned diametrically to each other. If forced air outflow will be used, it is advisable to make the supply hole higher than the exhaust hole. If it is possible to construct a ventilation system in which the air flow comes from below, heats up from the stove, rises up, and then goes outside, then installing additional fans will not be necessary.
When using fans Both the supply and exhaust openings should not be located at the same level. The air flow can be closed, which will lead to a concentration of cooled air masses below, while it will be too hot at the top.
It is not advisable to place an exhaust opening in the ceiling. When the incoming air goes up, you will have to spend a lot of time sufficiently heating the room. Warm air quickly rises, mixing little with cold air, and quickly leaves the bathhouse. You can vent the air upward in the dressing room if the goal is to heat it from the steam room.
Section of openings for ventilation should be related to the total area of the bathhouse or steam room separately. The holes should not be made too small. If ventilation is insufficient, it will take a long time for the air to be renewed, it may become too humid, and mustiness appear.
Ventilation diagram in the steam room of a Russian bath.

Ventilation in the washing room
As in the steam room, there is also a large accumulation of moisture in the washing bath. To avoid constant damp air, which leads to the appearance of fungi and mold, it is necessary to ensure its timely removal to the outside. A lot of water often accumulates under the floor, so for good ventilation it is often enough asbestos pipe. It can be placed in a corner. One end of the pipe is placed under the finished floor, and the other ends on the roof; it must be equipped with a deflector.
The construction of moderate, controlled ventilation allows you to keep the bathhouse dry, maintain a moderate temperature, get rid of humidity, and constantly inhale renewed, fresh air. Ventilation regulates the direction and location of the air inlet and outlet, the removal of carbon monoxide, and provides savings on fuel for the furnace.
Ventilation in the bathhouse is simply necessary. First of all, ventilation is intended to ensure the safety of people who take bath procedures.
Everyone knows that when breathing a person inhales oxygen and exhales carbon dioxide. In tight indoors After some time he will begin to choke. And in the steam room, where heat and the concentration of water vapor, this will begin to happen even faster.
Relaxing on the shelf, you won’t have time to get to the rescue one. The cost of an incorrect ventilation device can be prohibitive.
The second important factor is wood rotting. Enjoying and benefiting from bath procedures while smelling rot and mold is very problematic. Therefore, proper ventilation in a Russian bathhouse is the key not only to its benefits, but also to the health of vacationers.

The photo shows wood rotting due to insufficient drying of the wood
Experts believe that a ventilation device in a bathhouse in which the air in the room is changed three times in one hour can be considered correct. The ventilation scheme in the bathhouse is selected depending on the type of structure and materials used in the construction of the walls.
General principles of ventilation in a bathhouse
The correct design of a bathhouse and ventilation in it, regardless of the type of structure, is based on the following basic principles:
- The fresh air that enters the steam room should not disturb its temperature regime;
- Exhaust air, which contains the most carbon dioxide, must be removed from the room;
- The arrangement of air in the steam room should be layered: the hottest air is under the ceiling, on the bench it is as comfortable as possible and the coldest air is near the floor.
Note!
There should be no draft in the steam room!

If all these principles are followed, then bath procedures will bring the maximum effect for which they are designed - restoration of mental and physical strength.
Ventilation device in a free-standing wooden bath
The tree is considered ideal building material for a bath. Wooden walls “breathe”, so the issue of air exchange is partly solved naturally.
However, even in a wooden building in a steam room, ventilation is necessary. At a minimum, for quickly drying the wood after taking bath procedures.
Work plays a major role in air exchange processes sauna stove. When water is poured onto a column of hot steam is created, which rises upward. As it cools, it lowers, pushing the used air out of the steam room.

Together, the above factors allow you to create in the steam room required humidity and temperature, and ensure normal air circulation.
Let's take a closer look at the ventilation system in wooden baths. The main tasks for us, naturally, will be to ensure the flow of fresh air and the removal of exhaust air. Our instructions will help you cope with these tasks.
Ensuring air flow
The correct log house is laid in such a way that lower crowns were free. With this installation, access to fresh air from the street is ensured.
In addition, around the steam room door, in any case, there will be gaps sufficient for its entry. The stove in such baths is placed closer to the door so that it heats up immediately.

If the steam room is designed for 6 or more people, a separate air duct is connected to the heater, which supports the combustion process. If you make this air duct double, then the problem of fresh air supply is solved once and for all.
Exhaust air removal
If the heater is heated directly from the steam room, then the exhaust air is exhausted through the firebox into. At correct installation oven, no additional holes required.
In order to dry the room after completing the bath procedures, a small hole (up to 200x200 mm) can be cut in the wall. During the heating and operation of the steam room, it is closed with a special plug.

If the steam room has a window, such a hole is not needed. Sometimes a window from the steam room is cut into the washing room, and in the washing room either a through hole to the street or another window is made. Thus, when drying, two birds are killed at once, both the steam room and the washing room are dried.

Thus, the myth that ventilation is not needed for a wooden bathhouse is confirmed if the following conditions are met:
- The steam room is designed for 2-4 people;
- The lower crowns of the frame are laid freely;
- The stove-heater is heated directly from the steam room;
- There is a hole or window in the wall for ventilation.
Actually, such family baths are usually built on personal plots.
Ventilation device in a free-standing brick bathhouse
A brick structure, as well as a structure made of foam concrete, expanded clay blocks and other permanent structures, is another matter. Ventilation in brick bath more complex.
The first difference is that floors in a brick building must be ventilated. The thing is that the floors in the bathhouse are constantly in contact with water, and if they are solid, then the boards will have to be replaced approximately every three to four years. You don’t even have to talk about unpleasant odors and mold.
Ventilation of the floor in the bathhouse is laid at the stage of foundation construction. To do this, special holes are made in the foundation on opposite sides. These holes will provide through air circulation under the floor and drying of the joists.

The second difference is the mandatory presence of special supply and exhaust openings in the steam room. There may be several of them. Two supply holes are made at floor level and covered with grates to prevent rodents from entering.
There are 4 most popular schemes for ventilation in a bathhouse, from which you can choose the most suitable one for you.
- Scheme No. 1. The supply hole is located behind the stove at a distance of 50 cm from the floor. An exhaust hole is cut in the opposite wall no higher than 30 cm from the floor. A bath fan is installed on it, which will ensure air circulation.

According to this scheme, the air in the steam room is heated evenly, the incoming air is heated by the stove and rises. As it cools, it falls down and exits through the outlet. The lower it is located, the stronger the air flow will be. When using a fan, a ventilation valve can be installed at the outlet.
- Scheme No. 2. Suitable for those baths where the stove is heated from the steam room. In this case, the influx is made directly under the stove. The flow of fresh air is sucked in by the stove, supporting combustion, and provides an influx directly into the room.

The exhaust vent is located above the floor and connected to it corrugated pipe, which rises up to the roof level and opens onto the street. In other cases, the ventilation duct is made in the wall.
Note!
If the walls of the bathhouse are made of expanded clay concrete blocks, then ventilation ducts It is best to lay it during construction.
- Scheme No. 3. According to this scheme, ventilation for the bathhouse is arranged through cracks in the floor. In this case, the supply hole is made in the wall near the stove at a height of 30-50 cm from the floor. The air, heating up, rises and exits through the cracks between the floor boards into the basement. It is thrown out from the basement space using a special pipe.

Note! For normal functioning For this type of ventilation, it is necessary to leave gaps between the floorboards of 5-10 mm.
- Scheme No. 4. This scheme is suitable in cases where the stove also heats other rooms.

Fresh air is sucked in by the stove through holes in the floor and, passing through the firebox, goes out into the steam room and into the washing room. It is removed from the premises through openings located below, above the floor level.
There are also combined ventilation schemes, but to install them yourself, you need to consult with a specialist.

The video in this article will help you understand clearly how ventilation is arranged in a bathhouse.
It is impossible to answer the question of whether plastic ventilation is possible in a bathhouse. Such systems have proven their practicality and performance in home and industrial environments, but the bath environment has its own specifics, which to a certain extent limits the use of plastic. When choosing plastic products for a bath in each specific case should be approached taking into account all influencing factors and possible consequences.
The bathhouse can use plastic pipes for ventilation in the bathhouse
Reasons for the popularity of plastic
Ventilation structures made of plastic elements have gained wide popularity in a variety of areas. human life. This is due to their attractive appearance and numerous advantages over traditional metal competitors.
Note! The most widely used parts are made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyurethane and polypropylene.
The following stand out: positive sides plastic ventilation:
- No corrosion. This advantage most often determines the choice of plastic. Any metal (even stainless steel) in ventilation systems where steam condensation occurs, aggressive influences various substances air pollutants and are susceptible to corrosion. Plastic is absolutely resistant in this regard.
- Low cost. Plastic systems have significantly more low price compared to metal, which provides increased resistance to corrosion.
- Simplicity and quality of installation. During installation metal boxes and pipes, problems always arise in places where there are knocks, requiring rolling, welding, and other operations. Cutting and joining plastic elements is not difficult, and the ends are easy to process and align. Thus, sealing plastic boxes much easier to provide.
- Light weight. This advantage is ensured by ease of installation at the installation site and transportation when delivering the goods.
- Plastic elements are resistant to water, steam, aggressive environments, and ultraviolet rays. They match everything sanitary standards under normal conditions.
 Installation of PVC pipes for ventilation
Installation of PVC pipes for ventilation Features of use in the bath
In order to decide whether plastic ventilation is suitable for a bathhouse, it is necessary to note the disadvantages of such systems:
- Low heat resistance of plastic. Already at temperatures above 80-85 degrees, the release of harmful components from the substance that poisons begins human body. When heated, plastic loses its strength and rigidity, which leads to deformation.
- Low resistance to open fire. Despite the fact that PVC does not support combustion, it easily melts, and its drops, falling on other structures, cause a fire. In general, plastic elements belong to the group of flammable materials, which requires great care when placing them near the sauna stove and chimney. Even with a small fire, a large amount of acrid smoke is released, which is very dangerous for humans.
- Reduced resistance to cutting, abrasion, scratching. Under impact and cutting loads, plastic is easily damaged or deformed.

Taking into account the above problems, we can conclude whether plastic ventilation is suitable for a bathhouse. The most extreme conditions celebrated in the steam room. In the Russian bath, the temperature is maintained at about 60-65 degrees with saturated water vapor. Such temperatures seem to be lower than permissible, but they are close to critical values, and at the slightest excess they lead to the decomposition of plastic. Thus, the use of plastic ventilation in the steam room of a Russian bath is dangerous to human health. It is completely unacceptable to use it in a sauna steam room, where the temperature can reach 100 degrees.
 Smoke from burning plastic is very corrosive and can lead to poisoning.
Smoke from burning plastic is very corrosive and can lead to poisoning. In others bath rooms (washing department, dressing room, rest room) the air temperature does not have large values, and extreme conditions are associated with high humidity, which is not at all dangerous for plastic. Therefore, we can conclude that ventilation in a bathhouse made of plastic pipes is quite acceptable in all rooms except the steam room.

Important! Particular attention should be paid to the location of the stove and its chimney, near which the air temperature may be critical. In addition, fire hazardous conditions arise here.
 Particular care must be taken with the location plastic pipe for ventilation in the bathhouse. It is better to place it behind a brick lining if it is located near the stove.
Particular care must be taken with the location plastic pipe for ventilation in the bathhouse. It is better to place it behind a brick lining if it is located near the stove. Design features
In a standard bath set forced ventilation includes the following main elements: fan (exhaust and supply); ventilation pipes and boxes; vents with plugs; connecting and component elements. Among the important components, the following stand out:
- turns: designed to change the direction of the ventilation duct;
- adapters: necessary when connecting route elements of different sizes;
- forks and tees: installed when it is necessary to divide the incoming air flow into several rooms;
- couplings: connecting and holding elements;
- flanges and gearboxes.

The basis of forced ventilation is made up of exhaust type fans installed on the outlet vent, or the supply type, designed to suck in fresh air from outside and form an air flow. The most commonly used supply system is a fan that can be installed alone to serve all rooms or several devices separately in each room. In the first case, a fairly powerful mechanism is installed, usually with metal blades, and the flow distribution then proceeds through plastic ventilation channels. Small fans in a plastic case with plastic blades can be installed in each room.
 Plastic fans are used for exhaustion in the sauna.
Plastic fans are used for exhaustion in the sauna. Plastic air ducts for ventilation of the type of bath in question are an important part of the system. They distribute the incoming air flow and direct it to the desired area.

Another option is to install an exhaust fan not in the outlet vent, but directly in the most stagnant area. In this case, it is mounted at the end of the exhaust ventilation duct, through which polluted air is directed outside.
Plastic boxes and pipes are produced various shapes and sizes. They can be round or rectangular in cross-section, and smooth or corrugated in design. Most often, the incoming powerful air flow is directed into rectangular boxes and then distributed through round pipes.
Nuance! Corrugated construction is used in places where pipe movement in different directions is required, or to adjust elements to length.
 Types of composites connecting elements ventilation system
Types of composites connecting elements ventilation system Air ducts have various sizes, which are selected depending on the required system power and the volume of incoming air. Round pipes for a bath they have a standard diameter in the range of 56-160 mm. Among rectangular ducts, the most common are air ducts measuring 6x12 and 6x20.5 cm. Corrugated elements usually have round shape, and the diameter of such a pipe ranges from 15-55 cm.
 Plastic air ducts for ventilation they come in round and rectangular shapes
Plastic air ducts for ventilation they come in round and rectangular shapes Additional items
In addition to the indicated elements used when installing the ventilation system in the bathhouse, they are used plastic parts, performing protective and regulatory functions. These include various dampers, hatches and grilles.

Plastic grilles can have different purposes. The following main varieties are distinguished:
- inertial type: for flow separation without pressurization;
- adjustable grilles: allow you to change the volume of incoming air and distribution in one direction while blocking air movement in the other;
- unregulated type: distribution or flow restrictions without the possibility of regulation;
- external protective grilles: to prevent foreign bodies from entering the channel.
 Hood grates can be of an adjustable type
Hood grates can be of an adjustable type Plastic hatches can be installed in powerful, branched systems to allow access to the ventilation line for inspection, cleaning, and repair. They can be mounted on the ceiling or walls of the bathhouse. Door-style flaps are designed to allow access to natural flow. They can be mounted on natural ventilation vents in a window or door. Standard sizes are 10x10, 15x30 and 25x60 cm.
Features of the arrangement
You can install plastic ventilation in a bathhouse yourself. Main stages of work: production of vents; installation of fans; installation and fastening of the entrance box; installation and fastening of the incoming air flow branching system; arrangement of an outlet vent; installation of dampers and hatches.

When carrying out work, the following recommendations should be taken into account:
- The plastic elements are connected to each other by soldering. If there are threaded elements, sockets, flanges, adapters, and couplings are used, which makes it possible to provide a dismountable system.
- A special sealant is used to seal the joints.
- Cutting elements or changing their shape is done using a knife or a special hacksaw.
 Connection diagram of the fan section in a forced ventilation system
Connection diagram of the fan section in a forced ventilation system To carry out installation work, you will need the following tools: electric drill, screwdriver, grinder, knife, hacksaw, pliers and side cutters, screwdriver, paint brush, tape measure, metal ruler.
 Before use, it is necessary to check the ventilation system in the bathhouse
Before use, it is necessary to check the ventilation system in the bathhouse Plastic ventilation in the bathhouse can be installed in all rooms except the steam room. Plastic cannot be used in it due to the risk of harmful emissions when heated. You can easily install the system yourself.
A well-equipped ventilation system, all other things being equal, guarantees, firstly, a long service life of the building and finishing materials used in the arrangement of the serviced premises, and secondly, the comfort and safety of visiting the latter for the user. The issue of arranging complete and sufficiently effective ventilation is especially relevant in the bathhouse, due to the characteristic temperature and humidity conditions and additional requirements requirements for buildings of this kind.


Prices for bath fans
bath fan
Video - Requirements for ventilation in the bathhouse
Choosing the optimal type of ventilation system for servicing a bathhouse is a topic for many hours of discussion. For example, there is natural ventilation. The expenditure of money, time and effort on its arrangement is minimal - the work literally comes down to drilling holes in the walls, installing boxes/pipes and valves/grids.

 Ventilation valve and grille
Ventilation valve and grille  Ventilation grilles for baths and saunas
Ventilation grilles for baths and saunas 

However, it is impossible to use natural ventilation to service all rooms of the bathhouse. Of course, it would be possible to save money, but the disadvantage of such a solution will become obvious with the arrival of the first winter: along with the influx of fresh air from the street, cold will come in, and everyone knows the combination of frosty air with humidity - everything around will simply freeze. Therefore, natural ventilation in some rooms must be combined with other existing options in other rooms of the bathhouse.
If the bathhouse is equipped with a washing room or even its own swimming pool, natural ventilation will definitely not cope with the maintenance of such premises - it will have to be equipped exhaust system. And in general, the presence of a forced inflow/outflow of fresh air will be useful both for visitors to the bathhouse and for its premises. Recommendations regarding the optimal composition of the air exchange system are given in the table.
Table. Choosing a ventilation system for different rooms
| Room | Recommended ventilation type | Scheme | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steam room, dressing room or relaxation room | Aeration should be understood as organized natural air exchange. The option is most optimally suited for use in a bathhouse: air enters from the bottom of the stove (for other rooms - 25-30 cm above the floor), exhaust is discharged through an opening in the upper part of the room. The work of air exchange is based on elementary physical laws: cold air from the street displaces warm air masses, which have less weight, to the top of the room. Aeration is ideal for use in rooms with high heat output. The presence of additional humidity contributes to an even more pronounced increase in the efficiency of the system. |
||
| Wash room, bathroom, room with swimming pool | The system is equipped with a fan and, if necessary, cleaning filters. Mechanical exhaust ventilation is ideal for use in the washroom, pool room and other wet and frequently visited areas of the bathhouse. Mechanical hood provides effective removal unpleasant odors and excess moisture, which makes the air in the serviced area safe and clean. It is impossible to use exhaust ventilation alone - air rarefaction is formed. To compensate for the vacuum, an air flow from the street or other rooms is arranged. Along with this, the presence of supply ventilation will eliminate the likelihood of drafts. The supply ventilation system can be either natural or mechanical. In combination with mechanical exhaust ventilation It is more expedient to use a mechanical supply system, because the possibilities of natural inflow may ultimately be insufficient to compensate for the resulting rarefaction. Mechanical supply ventilation is based on a blower fan. Additionally, it can be equipped with an air heater, which will eliminate inconvenience and solve the problems of ventilation of serviced premises during the cold season. Additionally, the supplied air can be humidified or purified using appropriate devices. A mechanical system is more complex in arrangement compared to its counterpart, which operates according to the laws of physics: in addition to fans and air ducts, the system may include optional equipment and accessories (diffusers, air distribution grilles, automation equipment, noise suppressors, etc.). This provides an excellent opportunity to design an air exchange system that fully meets the user’s wishes. |
Natural ventilation is provided in vestibules, warehouses and other similar premises.
Regardless of the type of ventilation system chosen, the bathhouse must have conditions for simple ventilation. Install adjustable windows in all rooms, the location of which allows this to be done.
Video - Types of ventilation systems
Instructions for self-calculation of air exchange
An elementary formula is used for calculation:
W (required volume of fresh/exhaust air) = k (coefficient indicating the frequency of air exchange) x V (volume of the room served, determined by multiplying the width of the room by the length and height).
That is, first you must calculate the volume of each room and find for it the required indicator of the volume of clean air (in calculations it is usually denoted Wpr, i.e. inflow) and a similar indicator of exhaust air (denoted as Wout, outflow). In this case, multiplicity factors must be taken into account. The calculated values are rounded upward - the last digit in the number must be 0 or 5.
Next, the summation of all Wpr is performed. A similar action is carried out for the found Ww. The resulting amounts are compared. If the total value of Wpr exceeds the total value of Wpr, you need to increase the exhaust volume for rooms with a minimum air exchange value, if, on the contrary, increase the inflow by the missing value. That is, at the output, the sum of all Wpr should be equal to the total value of the found Wt.
The results of the calculations will allow you to determine the optimal cross-sections of the installed air ducts and select the appropriate type of ventilation system. Thus, there will not be any special problems with calculating the volume of premises and other related data. For greater convenience of subsequent processing, enter the found values in a simple table, as in the example presented.

In the example given, the total value of Wpr is less than the sum of all found Wt by an indicator equal to 110 m3. In order for the balance to be maintained, it is necessary to ensure an influx of clean air in the missing quantity. This can only be done in the waiting room. Thus, the value of 55 m3 for the dressing room given in the table must be replaced with an indicator of 165 m3. Then the balance will be maintained.
Start calculating the air ducts to be installed and drawing up the structure of the ventilation system being installed.
The ventilation system is designed in such a way that the air moves through the installed air ducts at the following speeds:
- ≤ 5 m/s in main ducts and ≤3 m/s in existing branches – for mechanical ventilation systems;
- ≤ 1 m/sec – for air exchanges operating on a natural principle;
- 2 m/sec – for natural air exchange directly in the steam room.

When choosing the cross-section of air ducts, take into account the above indicators. As for the profile of the duct/pipe, this point is determined by the design features of the air exchange and the bath itself. For example, air ducts with round are easier to install compared to their rectangular “counterparts”, and it is much easier to select the required connecting fittings for round air ducts.
The relationship between the diameter of the air ducts and other significant indicators is demonstrated in the following tables.


For example, we will work with round air ducts. We select the required sections according to the appropriate table, focusing on the indicators in the table Example of ventilation calculation.
The calculated air flow was 165 m3/hour. The air flow at this flow rate should move no faster than 5 m/sec. In accordance with the table above for round air ducts, we select the cross-section according to the specified data. The table value closest to ours is 221 m3/hour. The air duct cross-section is 125 mm.
 Air duct with insulation
Air duct with insulation  Flexible ducts
Flexible ducts
In the same order, we determine the optimal sections for all branches of the system in the serviced premises, remembering that the air flow in them should move at a speed not exceeding 3 m/sec (in vestibules and storage rooms - 1 m/sec, in the steam room - 2 m/sec sec):
- steam room: calculated Ww is 60 m3/hour, which requires the installation of an air duct with a cross-section of 125 mm;
- shower room - Ww is 50 m3/hour, air moves at a speed of 3 m/sec, a 100 mm air duct is suitable;
- toilet – indicators are similar to the shower room;
- pantry, vestibule, etc. – indicators (except for air speed) are similar to shower and toilet.
Important! In the shower room (wash room, room with a swimming pool) there is an increased level of humidity. When determining the cross-section of the air duct for this room, it is necessary to make an adjustment towards increase (in this example - 125 mm).
For greater convenience, enter all the information received into the table. You can use the template below as an example.
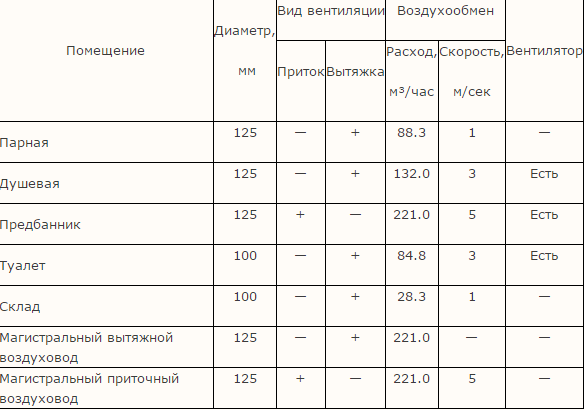
Important note! In the table above, the exhaust volume exceeds the volume of incoming clean air. This happened for the reason that the sections were determined by the nearest flow rate, and the diameter of the air duct in the washing room was intentionally increased. In practice, such an approach will only be beneficial - the margin for outflow and inflow will not be superfluous.

SNiP 2.08.01-89. Residential buildings. File for download
Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for residential buildings and premises. Sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations SanPiN 2.1.2.1002-00. File for download
Construction norms and rules of the Russian Federation heating, ventilation and conditioning SNiP 41-01-2003. File for download
Square cross section the ventilation window is determined in accordance with the volume of the room served: 24 cm 2 for every 1 m3.
All that remains is to deal with optimal height location ventilation holes:
- for the flow of fresh air - on average 25-30 cm above the floor (in the steam room - near the stove);
- for exhaust air outflow - approximately 15-20 cm below the ceiling, usually on the opposite wall to the supply wall.
Popular bath ventilation schemes
Only options for arranging ventilation in the steam room deserve special consideration - in the remaining rooms everything is done according to the standard scheme, for example, like this:

Air exchange in the steam room can be organized in accordance with 4 main schemes presented in the following image.

Scheme "a". The most popular option. The window for air flow is next to the stove, at a distance of about 25-30 cm from the floor. Incoming fresh air gradually displaces the waste heat upward to the opposite wall. There is an exhaust hole on it, approximately 15-25 cm below the ceiling.
Scheme "b". Both holes are on the same wall. The circuit will only work if you install an exhaust fan. Fresh air enters through the lower hole, located in the wall opposite to the stove. The air will rush in the direction of the stove, and then, covering the space of the steam room in an arc, move to the hood and be discharged outside the bathhouse.
Scheme "c". This option is suitable for steam rooms with leaking floors. The inlet hole is located as in diagram “a”. Having warmed up in the upper part of the steam room, the air descends to the floor, passes through the gaps in the plank flooring, facilitating more efficient drying of the boards, and is then discharged through an exhaust vent, usually located in another room. Exhaust can also be carried out through a separate isolated channel.
Scheme "g". Option for baths with a constantly running stove. In this case, the exhaust function is performed by the furnace ash hole. The supply window is located under the shelf, in the wall opposite to the stove. The height of the inlet opening must correspond to the height of the furnace vent. Fresh air rushes towards the stove, displacing the air masses heated by it to the ceiling. Cooling there, the air descends and is removed from the bathhouse through the ash pan.
To ensure that the air exchange system operates as efficiently and as efficiently as possible, before starting its installation, study and remember a few simple tips.
If your bathhouse has a bathroom or even a kitchen, equip them only with exhaust ventilation - this solution will eliminate the possibility of unpleasant odors spreading to other rooms. As an alternative, you can install fresh ventilation in other rooms, and equip the bathrooms with natural exhaust - in this case, the air will move towards the bathrooms.

When calculating fan performance, it is recommended to reduce the total power air supply devices by 5-10% of the total productivity of exhaust units. In this case, the exhaust air will be completely replaced by incoming air masses, and a reserve of 5-10% will compensate for the influx of air entering through windows, cracks, etc., which will allow a balance to be maintained.

In rooms with only natural ventilation, it is recommended to make opening windows - this will increase the efficiency of fresh air supply and reduce the risk of fungi, mold, rot, etc.

Important! If your bathhouse has a non-standard configuration, the design of the ventilation system will also be individual. When compiling it, the features of the composition of the premises, their design, design features, etc. should be taken into account.
The main stages of independent installation of a ventilation system
Any ventilation system in any room is installed in approximately the same sequence. The differences are present only in the characteristics of the air duct openings and their locations, as well as the configuration of the system (mechanical, unlike natural, are supplemented with various types of devices).
For example, the following arrangement of ventilation elements can be used.

Or its slightly modified analogue, shown in the following image.

Recommendations regarding the choice of the location of each opening, the type of air exchange system for different rooms of the bath, as well as the procedure for determining the characteristics of ventilation elements, were discussed earlier.
Along with this, the procedure for arranging ventilation may vary depending on which design option you prefer. There are few solutions available:
- independent ventilation in each room. A simpler option. Work is limited to the installation of transoms, vents, fans and other necessary elements, if provided for by the project. Fans can be mounted both in windows and in separate ducts led outside through the wall;
- centralized system. More difficult option. Requires installation of ventilation ducts. Used mainly in private homes - in the case of a bathhouse this option will be too costly and labor-intensive;
- "hybrid" option. Some rooms are ventilated individually, others are combined into a joint system.
An appropriate option for use in a bathhouse is independent ventilation - the owner can choose the optimal characteristics of fans and other elements for each room, saving money, time and effort on carrying out the activities necessary to combine the channels into a single system.
Important! The location of some bathhouse premises may not allow for the establishment of an independent supply and exhaust ventilation. In this case, it will not be possible to avoid laying ventilation ducts. Alternatively, the boxes can be placed in the attic, and the ventilation holes can be installed in the ceiling or connected to channels installed in the walls (the option is more complicated if the installation of such channels was not provided for by the project at the construction stage of the bathhouse).
In most cases, the first option is used: ventilation pipes of the required length are led out through holes in the ceilings of the premises served and are either equipped with their own fan, if necessary (easier to implement for an untrained user, the procedure is similar to that shown in the following table), or are connected into a single circuit and connect to a common hood (may require the involvement of specialists).
Remember: maximum efficiency The operation of the ventilation system is ensured by using the shortest and straightest air ducts possible - up to 3 m when arranging natural air exchange and up to 6 m when using electric fans.


The procedure for installing an independent ventilation system is given in the following table.
Important! The example describes instructions for arranging a mechanical ventilation system using fans. The installation procedure for natural air exchange remains almost the same: only the stages of laying wires and installing fans are excluded.
Table. Ventilation arrangement
| Work stage | Explanations |
|---|---|
| The operating procedure remains the same for the supply and exhaust openings. Only the height of their arrangement and location changes ( possible options discussed earlier), as well as the type of fans used (supply or exhaust). The characteristics of the latter are selected individually, taking into account the volume of the room served, the required speed of air movement in the air ducts, the required air exchange rate, etc. – all these points were covered in the theoretical part. We arrange the holes in the following order: - outline the center and contours. We make the markings so that the resulting diameter of the hole slightly (usually a 2-3 mm gap is made) exceeds the diameter of the pipe being installed (recommendations for choosing the diameters of air ducts were given earlier); - using a puncher we make a hole in accordance with the markings. We hold the working tool horizontally, but with a slight downward tilt; - carefully take out the cut material (a hammer and chisel will help us with this), after which we carefully clean the finished hole from dirt and dust. |
| The ventilation pipe (ventilation duct body) is placed in the prepared hole, but before that it (if mechanical/forced ventilation is planned) must be equipped with a fan. Useful recommendation! Initially, buy ready-made kits for arranging ventilation, including, in addition to related additions, a ventilation duct/pipe and a fan with a housing of the appropriate size - this way you will avoid difficulties at the assembly stage. The pipe with the fan is placed in the prepared hole, and the remaining cracks are filled with foam. |
| The fan is electrical appliance, therefore, it needs to be connected to the network. Let's do this while the mounting foam dries (at least 10-12 hours). The procedure is standard: - the contours of the groove for the cable are cut out in the wall using a grinder. Excess material is removed using a bumper; - a hole is prepared in the wall for installing the switch box (for example, you can use a hammer drill). The box is installed (pre-read the instructions specific to your switch). The switch itself will be mounted after finishing; - the wire is laid in the groove. To fix the cable we use alabaster; - connect the wire to the switch and the fan. First, be sure to study the connection diagram recommended by the fan manufacturer in the attached instructions, because For different devices it may differ. As an example, one of the most commonly used schemes is given. |
| All that remains is to bring the entire structure into proper form. To do this we do the following: - get rid of excess dried polyurethane foam using a knife; - putty the grooves; - we install adjustable ventilation grilles on both sides of the pipe. For fastening we use self-tapping screws. If provided, at the appropriate stages of work we install additional elements(for example, air heater, filter, etc.). Each of these devices is installed individually - we first clarify these points in the manufacturer’s instructions. |
Video - Arrangement of ventilation holes
Video - Ventilation in a bathhouse with your own hands - diagram








