The modern refrigerator market is quite saturated - this is explained by high competition, which is associated with the presence of foreign manufacturers in Russia, of which there are many. This, in turn, sets the pace for the development of new technological and design solutions, which could “hook” a potential buyer. However, in 2015 there was a decline in sales for reasons known to all, this also applies to online sales of refrigerators. Buyers began to look closely at less famous manufacturers - their products usually cost less. Concerning domestic producers, their share of sales is still at a low level.
But not only price is a decisive factor when choosing a refrigerator. For example, buyers are often hesitant to make a choice because they are not sure which technology solutions are best for them. In particular, this applies to the popular No Frost and Low Frost cooling systems.
Cooling system No Frost
Thanks to this technology, you can almost completely forget about defrosting the refrigerator, as well as frozen, frost-covered walls. This system works as follows.
With the help of a fan, flows containing cold air are evenly distributed throughout all chambers of the refrigerator. Getting into the evaporator, these air flows lose some of the moisture, which, in turn, turns from vapor into liquid (droplets). They settle on the walls and turn into frost. But it doesn’t stay there for long - the frost melts as a result of the heating element’s operation, and flows into the pan in the form of water droplets. But the thawed liquid does not accumulate in the pan either - it evaporates.
The technology is applied to all refrigerator compartments.
Disadvantages of No Frost technology
- Increased energy consumption. As they say, convenience comes at a price.
- Such refrigerators are noisier (but not critical), especially if we're talking about about budget models.
- Cooling occurs due to forced circulation air flows. In this regard, almost all moisture leaves the refrigeration chambers. If you store food unprotected (not covered, without packaging, etc.), they will dry out greatly, which will not have the best effect on their properties.
Cooling system Low Frost
The basis of this technology is an evaporator located around the entire perimeter of the inner walls of the freezer. This allows you to keep temperature and humidity at approximately the same level. In addition, the process of ice formation on the walls is very slow, and the ice itself “grows” lightly, thin layer. This makes defrosting much easier. And although it will still have to be done manually, it will take much less time compared to conventional refrigerators that do not use this technology.
Disadvantages of Low Frost technology
- Sometimes you still have to defrost.
- The technology only applies to the freezer. It is not used in the refrigerator compartment.
No Frost or Low Frost - which is better?
Both technologies are good in their own way. Which one is better should be determined by each individual, taking into account individual needs. Knowing about the features of these two cooling systems, making a choice will be much easier.
No Frost Ideal for those who do not have the time or desire to defrost their refrigerator, as well as for those who are ready to ensure that food is well packaged and protected from drying out. Products will last longer due to cold and low humidity levels. In such conditions, bacteria multiply much more slowly.
Low Frost is a compromise solution. IN freezer a “fur coat” consisting of a thick layer of frost and ice will not grow. And even if the light goes out in your absence, you won’t have to worry about a possible flood. Minimizing temperature changes and maintaining uniform humidity helps preserve food well without the need for additional covering. It will be necessary to defrost the freezer extremely rarely, and then only by and large, for hygienic cleaning. In addition, this process will not take much time due to small quantity ice.
After visiting the store household appliances or having glanced at the numerous selection of models of refrigerators and freezers in the online store, you probably noticed their characteristics, namely " Frost Free"or "Full no Frost"? A direct translation from English will not always answer the question - do you need it? Let's clarify the situation. Let's start with a banal translation: No Frost - no frost! This means that refrigerators equipped with the No Frost system are not susceptible to the creation frost on the internal working surfaces. Consequently, such a system eliminates manual defrosting, thereby easing the fate of the user. Without going into the small details technical details different manufacturers, then two types of No Frost systems can be distinguished: Partial
Full
Partial implies the presence of a “no frost” system in only one of the refrigerator compartments, namely the freezer. In this case, the refrigerator compartment is defrosted using the drip type. This system is also commonly called Frost Free. Complete No Frost, unlike partial, covers the entire refrigerator with its effect. How does the No Frost system work? Let's start with the fact that the literal translation of “NO frost” does not entirely correspond to the truth, because the formation of frost on surfaces that have a lower temperature than the surrounding air is a physical process. But the laws of physics have not yet been canceled! Therefore, the words absence of frost should be understood not as the absence of frost as such, but its invisibility for the user. Frost forms on surfaces that are not accessible to view, does not get in the way under your hands and does not occupy usable area. For example, if you open the freezer compartment of a refrigerator without a No Frost system, then on each shelf you can see the presence metal plate, consisting of tubes bent in a serpentine shape and interconnected by rods for structural integrity. This type of plate is called an evaporator or an air cooler. It is through these tubes that the refrigerant passes, and it is on them that frost forms, gradually developing into an ice coat that requires defrosting. Let's talk about defrosting the refrigerator evaporator. We all know very well that it is impossible to operate a refrigerator with a large coat of snow on the evaporator - firstly, there will be elevated temperature- products may spoil; secondly, the refrigerator will consume too much electricity. Therefore, “No Frost”, and “Frost Free”, and “Full no Frost” mean that the refrigerator operates without frost. But the concept of a “refrigerator without frost” cannot be taken literally. After all, the surface of the evaporator has negative temperature, and the atmospheric air is always humid - and under such conditions, moisture from the air will always settle on the cold surface of the evaporator and freeze. Thus, in the “No Frost”, “Frost Free” and “Full no Frost” systems we are not talking about the absence of frost as such, but about methods for defrosting the evaporator. Most of us still remember the “manual” defrosting of the evaporator. We turn off the refrigerator from the network, open the doors wide, take out all the food, wait half a day.. Today, the most common is the so-called “drip type of defrosting”. In such refrigerators, the evaporator consists of two parts. The main part of the evaporator is located in the low-temperature compartment, and another small part is located in the medium-temperature compartment. The mid-temperature evaporator, sometimes called a petal evaporator, is located either directly at the back wall of the refrigerator or is mounted directly into it, in which case it is sometimes called a “recessed evaporator.” How does the evaporator defrost in such refrigerators? The part of the evaporator, located in the low-temperature compartment, is thawed traditionally - in the old-fashioned way - manually. True, the real need to defrost this evaporator occurs once every 4-6 months. To understand the principle of defrosting the evaporator blade, remember that the refrigerator compressor turns on periodically. There are so-called working parts and non-working parts of the cycle. In the working part of the cycle, the compressor is turned on, the evaporator takes on a negative temperature and frost forms on it. When the compressor turns off, the non-working part of the cycle, the evaporator will begin to heat up from the air in the chamber (in the medium-temperature chamber the temperature is always positive), and the frost formed during the working part of the compressor cycle will thaw and the moisture, along special grooves, will flow outside the chamber into the bath above the compressor . Because of high temperature On the surface of the compressor housing, this moisture will gradually simply evaporate. Now about the “No Frost” evaporator defrosting system. Sometimes this type of defrosting is called “wind type defrosting.” In refrigerators with this type of evaporator defrosting, the evaporator itself has something completely different design(most often in the form of a coil with ribs) and is located either behind back wall refrigerator, or in a special compartment. A mandatory attribute of a refrigerator with a “No Frost” system is a fan, which ensures constant air circulation inside the cooled volume. Warm air from the cooled volume, through special channels, it is driven by a fan through the evaporator, cooled and, through other channels, returned to the refrigerating chamber. What will happen to the frost in such refrigerators? Naturally, during the working part of the compressor cycle it will freeze on the evaporator. During the non-working part of the cycle, the frost formed on the evaporator will be thawed using a small electric heater - a heating element, and removed outside the refrigeration chamber. In some models, the evaporator is defrosted periodically - after a certain period of time - 10-16 hours - the timer turns off the compressor and turns on the heating elements. For those who are especially curious, here is a photo of the evaporator of a refrigerator with the “No Frost” system. In this case - if the evaporator is with a fan - it is called an air cooler. We have figured out the principle of evaporator defrosting using the “No Frost” system. Now, briefly, about the features of the “Frost Free” and “Full no Frost” systems. In refrigerators with a “Frost Free” defrosting system, the “No Frost” system is installed in the low-temperature compartment, and the drip type of defrosting is used in the medium-temperature compartment - an evaporator petal is mounted. Refrigerators with "Full no Frost" have both low-temperature and medium-temperature compartments SEPARATE systems evaporator defrosting "No Frost". Thus, the “Frost Free” and “Full no Frost” systems are characterized only by the degree of use of the “No Frost” system. The usefulness and effectiveness of the "No Frost" defrosting system can only be determined by comparing it with a more traditional drip defrosting system. In other words, let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of this system. The advantage of refrigerators with the “No Frost” system: - uniform temperature conditions in the cooled volume. If in refrigerators with drip thawing the temperature difference along the height of the medium-temperature chamber can reach 5-6°C, then with the “No Frost” system it is 1-2°C; - high speed recovery temperature regime in a refrigerated volume after opening the door or loading a large quantity warm foods; - high speed of cooling and freezing of products. Disadvantages of refrigerators with the “No Frost” system: - due to the increased speed of air circulation, the shrinkage of unpackaged products increases. On the other hand, we are already accustomed to storing food in packaging, and the shelf life of food is generally short; - slightly increased electricity consumption due to the additionally installed air cooler electric motor. The additional electric motor also introduces additional noise and vibration. Although, in reality, the increase in energy consumption and the increase in noise and vibration are practically not noticeable; - the increased complexity and technical richness of refrigerators with the “No Frost” system leads to a slight decrease in their reliability.
On modern market everything remains fewer refrigerators and freezers requiring manual defrosting. This category includes only small single-chamber refrigerators domestic production, as well as a certain number of freezers of different brands.
If you are looking to purchase a medium to large capacity two- or three-compartment refrigerator (which is the type of model market research reports are in greatest demand), you are bound to come across terms such as “ automatic system defrost", "No Frost", "Frost Free". In this regard, we will try to understand the operating principles of modern refrigerators and identify the advantages and limitations of each type of defrosting.
Everyone probably understands that it is impossible to do without defrosting the refrigerator at all: the very operation of the compressor and cooling system in the refrigerator implies the formation of snow or frost on the inner walls. Manufacturers solve this problem in several ways.
Text: Elena Omelchenko
Well, the type is drip
As you understand, manual defrosting is rare for refrigeration chambers; they defrost automatically using the “drip” or “windy” type, while freezers defrost only using the “windy” type or manually.
The drip type of defrosting is used in most modern refrigerators. In this case, an evaporator is located on the back wall of the refrigerator compartment (sometimes it is built inside the back wall to save space, and then it is called a “recessed evaporator”). The function of the evaporator is to cool the rear wall of the refrigerator so that the formation of a layer of frost (ice) occurs only on it. When the compressor stops, the ice begins to melt, and the moisture flows down through special guide grooves into the drain, and from there into a special container (bath) located above the compressor.
The temperature in the compressor area is quite high, which ensures the evaporation of the resulting moisture. At this point the cycle ends, and everything repeats again. The defrosting process is carried out gradually, unnoticed by the users of the refrigerator, who can only notice at what stage of the defrosting cycle the refrigerator is currently in - this is indicated by the back wall, namely, whether it is frozen or covered with drops of water. The frequency and duration of defrosting cycles depend on the setting of the thermostat knob (temperature in the refrigerator compartment), the degree of load in the refrigerator with food, and the ambient temperature.
And this guy is very windy
The windy type of defrosting is generally referred to as the No Frost system. In refrigerators equipped with No Frost, the evaporator is removed from the refrigerator compartment and hidden in a housing behind the back wall of the refrigerator or above the freezer. In this case, the refrigerator is additionally equipped with one or more fans that ensure constant circulation of cold air inside the chambers. The fan blows on the evaporator, the air cools and blows through the chamber, entering it through special air ducts. The moisture generated during operation of the refrigerator does not freeze on the walls with a layer of frost, but “settles” on the coldest area - the evaporator.
The compressor is periodically turned off, and the layer of frost with which it is covered by that time is defrosted by a small heater, after which the resulting moisture evaporates again.
The No Frost system can be equipped with both refrigeration and freezer compartments, while only the refrigerator compartment is thawed using the drip type.
Any type of automatic defrosting will certainly save a lot of time for refrigerator users. Of course, you can’t do without defrosting: no matter how modern your refrigerator is, it is recommended to carry out preventive cleaning 1-2 times a year inner surface refrigerator when it is turned off, but, of course, you will no longer have to clean off 10-centimeter “snow caps” with a knife and ruler, as a decade ago.
No Frost - not so simple
So which model should you choose, what are the advantages and disadvantages of No Frost compared to drip-type refrigerators?
Experts about the advantages of No Frost:
More uniform distribution of cold air and, therefore, temperature throughout the entire volume of the refrigerator (freezer) chamber.
Faster restoration of the temperature in the chamber after loading a large batch of products inside or simply opening the door repeatedly (positively affects the quality of cooling and preservation of products, saves energy).
Both the first and second opinions are confirmed by the results of special tests of the Demand magazine: indeed, the difference in temperatures inside a refrigerator chamber equipped with a No Frost system does not exceed 1-2 degrees, while in drip-type refrigerators it can reach 5-6 degrees (from +2 on the lower shelves to +8 on the upper ones). An even more significant temperature difference is observed in freezers without No Frost (up to 7-9 degrees, as opposed to 1-2 with No Frost).
As for faster temperature recovery after opening the door, here, in addition to No Frost, the power of the refrigerator, determined by the number of compressors, and the quality of thermal insulation of the refrigerator walls, which becomes more and more advanced every year, play a role. At the same time, some experts express the opinion that refrigerators without No Frost maintain temperature longer during a power outage due to the absence of air ducts through which cold air can leak.
Among the disadvantages of No Frost are:Reduced humidity level in the chambers due to constant forced air circulation and, as a result, faster “drying” of products.
Reducing the volume of the refrigerating chamber due to the appearance additional equipment(it is calculated, for example, that No Frost “takes” at least 20 liters from the useful volume of the freezer).
Increased noise level during operation (simultaneous operation of the compressor and fan plus constant movement of air masses).
Increased energy consumption during operation of the refrigerator.
The higher cost of the refrigerator due to more complex design refrigerator and the presence of additional equipment (for example, fans).
The opinion about faster “drying” of products in refrigerators with a No Frost system, in our opinion, should not be decisive: there are indeed prerequisites for faster “drying” of products, but only if the rules for food packaging are not followed during their storage .
Research conducted by specialists from the magazine “Demand” showed, for example, that green salad leaves in both types of refrigerators begin to wither on the second day if they are not wrapped in a damp cloth. The same applies to the rules for storing cheeses, meats, dairy products, fruits and vegetables. Almost identical moisture losses were also noted during special studies on “test packages”.
The data on the higher noise level of refrigerators with No Frost is confirmed: so, if the standard two-compartment refrigerator operates at an average of 42 dB, then the noise level of refrigerators equipped with the No Frost system reaches an average of 45-47 dB. At the same time, a number of manufacturers (for example, Siemens) use fans of improved design (“low-speed”), in which case the noise level does not exceed the class average.
Refrigerators with No Frost are indeed somewhat more expensive than their “drip” counterparts, in addition, the presence of a large number additional elements increases the likelihood of product failure due to the breakdown of one of its structural elements.
At the same time, equipping a refrigerator with a No Frost system increases its class, and models with No Frost, as a rule, are positioned by the manufacturer as representing the middle and higher price categories, which increases the likelihood of using improved technologies and the presence of additional functions.
It should be noted that in some refrigerators there is a combination of a “crying” evaporator in the refrigerator compartment and a fan in the freezer. This combination is quite attractive from the point of view of a comprehensive solution to the problem, especially when used by most manufacturers modern technologies cooling.
These include, for example, multi-flow air supply systems (Multi Flow, Multi Air Flow, Super X-Flow, etc.), door cooling systems, the presence of a super cooling mode, etc. Whether it is a mandatory condition for you to equip your refrigerator with the No Frost system, decide for yourself - now you are fully equipped for this.
Let's start with a banal translation: No Frost- no frost!
This means that refrigerators equipped with the No Frost system are not susceptible to the creation of frost on the internal working surfaces. Consequently, such a system eliminates manual defrosting, thereby making the user's life easier.
Now let’s look at the types of “no-frost” systems and their technical design.
As a matter of fact, if you don’t delve into the fine technical details of different manufacturers, you can distinguish two types of No Frost systems:
- Partial
- Full
Partial implies the presence of a “no frost” system in only one of the refrigerator compartments, namely the freezer. In this case, the refrigerator compartment is defrosted using the drip type. Such a system is also commonly called Frost Free .
FullNoFrost Unlike partial, its effect covers the entire refrigerator completely.
So how does the system work? No Frost ?
Let's start with the fact that the literal translation of “NO frost” does not entirely correspond to the truth, because the formation of frost on surfaces that have a lower temperature than the surrounding air is a physical process. But the laws of physics have not yet been canceled! Therefore, the words absence of frost should be understood not as the absence of frost as such, but its invisibility for the user. Frost forms on surfaces that are not accessible to view, does not get in the way under your hands and does not occupy useful space.
For example, if you open the freezer compartment of a refrigerator without a No Frost system, then on each shelf you can see the presence of a metal plate consisting of tubes bent in a serpentine shape and interconnected by rods for structural integrity. This type of plate is called an evaporator or an air cooler. It is through these tubes that the refrigerant passes, and it is on them that frost forms, gradually developing into an ice coat that requires defrosting.
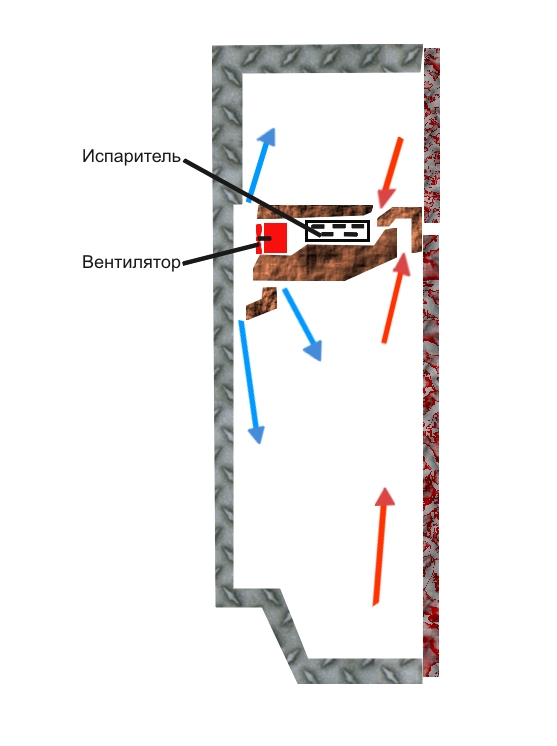
If you look into the same freezer compartment of a refrigerator equipped with a “no frost” system, you will not be able to find any tubes, and, therefore, there simply cannot be frost on them.
Where is the frost hiding? And it hides in the same place as the cooler itself, which in refrigerators with the No Frost system is hidden behind plastic panels. IN different models refrigerators and air cooler can be placed in different places. For example, in the first models of Indesit refrigerators, the evaporator was located in the upper part of the freezer, and in the latest models it is already hidden behind the back wall.
According to the principle of operation, the No Frost system resembles the operation of a conventional air conditioner, where air cooled by the evaporator is supplied into the room by a fan. Only in a refrigerator does a fan supply cooled air to a system of air ducts that distribute it throughout the freezer and refrigeration chambers(depending on model).
A completely logical question arises: where does the frost go from this hidden evaporator?
Agree that if a refrigerator with a “no-frost” system also needed defrosting, its benefits for the user would be highly questionable. And therefore, manufacturers have provided automatic defrosting of the air cooler over time. Periodically, every 10 - 16 hours, depending on the model, the frost on the evaporator is thawed with special heating elements located on it. The water formed as a result of the melting of frost is discharged through a special channel into a container attached to the refrigerator compressor. And since the operating compressor is at a high temperature (and this is exactly the case), this melt water safely evaporates, making room for the next defrost cycle.
Naturally, the presence of No Frost or Frost Free systems in the refrigerator has its advantages and disadvantages. But we will talk about them in the next article. In the meantime, thank you for your attention and good luck with your choice.
Many of us have heard that a refrigerator can have a “No Frost”, or “Frost Free”, or “Full no Frost” system. But not everyone knows what it is and, most importantly, do we need it?
These terms characterize refrigerator evaporator defrost.
It is known that it is impossible to operate a refrigerator with a large coat of snow on the evaporator. Reasons: - there will be an increased temperature in the chamber (food may spoil); and also the refrigerator will have increased energy consumption.
So, “No Frost”, and “Frost Free”, and “Full no Frost” mean that the refrigerator operates without frost build-up. More precisely, these methods characterize methods for defrosting an evaporator.
Not so long ago, there was only a way to “manually” defrost the evaporator: turn off the refrigerator from the network, open the doors wide, take out all the food, put the pan with warm water We're waiting for a few hours...
In low-budget household refrigerators Today the most common is the so-called "drip type defrosting".
In such refrigerators, the evaporator consists of two components: the main part of the evaporator is located in the low-temperature compartment (freezer), the other part is in the medium-temperature compartment.
The medium-temperature evaporator, sometimes called the evaporator petal, is located either directly at the rear wall of the refrigerator or is built directly into it - a “recessed evaporator”.
How does the evaporator defrost in such refrigerators?
The part of the evaporator that is located in the low-temperature compartment is defrosted manually. Although, it should be noted that in reality the need for defrosting occurs no more often than once every six months.
Defrosting of the evaporator blade occurs automatically during the period of time when the refrigerator compressor is not working - the so-called non-working part of the cycle.
When the compressor is turned off, the evaporator in the medium-temperature chamber will begin to heat up from the air in the chamber (in the medium-temperature chamber the temperature is always positive), and the frost formed during the working part of the compressor cycle will thaw and the moisture, along special grooves, will flow outside the chamber into the bath above the compressor. Due to the high surface temperature of the compressor housing, this moisture will gradually simply evaporate.
 Now about the “windy type of defrosting” - about the “No Frost” evaporator defrosting system.
Now about the “windy type of defrosting” - about the “No Frost” evaporator defrosting system.
Here the evaporator itself has a different design (most often in the form of a coil with fins) and is located either behind the back wall of the refrigerator or in a special compartment.
A prerequisite for a refrigerator with a “No Frost” system is the presence of a fan, which ensures constant air circulation. Warm air from the cooled volume, through special channels, is driven by a fan through the evaporator, cooled and, through other channels, returned to the refrigerating chamber.
In such refrigerators, frost will freeze on the evaporator during the working part of the compressor cycle. When the compressor is stopped, the frost formed on the evaporator will be thawed using the heating element. In some models, the evaporator is defrosted periodically - after a certain period of time - 10-16 hours - the timer turns off the compressor and turns on the heating elements.
We have figured out the principle of evaporator defrosting using the “No Frost” system. Now, briefly, about the features of the “Frost Free” and “Full no Frost” systems.
In refrigerators with a defrost system" Frost Free"In the low-temperature compartment, the "No Frost" system is installed, and in the medium-temperature compartment, a drip type of defrosting is used - an evaporator petal is mounted.
Refrigerators with " Full no frost" both the low-temperature and medium-temperature compartments have SEPARATE evaporator defrosting systems "No Frost".
Conclusion: the "Frost Free" and "Full no Frost" systems are characterized only by the degree of use of the "No Frost" system.
The usefulness and effectiveness of the "No Frost" defrosting system can only be determined by comparing it with a more traditional drip defrosting system. In other words, let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of this system.
The advantage of refrigerators with the "No Frost" system:
Uniform temperature regime in the cooled volume. If in refrigerators with drip thawing the temperature difference along the height of the medium-temperature chamber can reach 5-6°C, then with the “No Frost” system it is 1-2°C;
- high speed of temperature recovery in the refrigerated volume after opening the door or loading a large amount of warm products;
- high speed of cooling and freezing of products.
Disadvantages of refrigerators with the “No Frost” system:
Due to the increased speed of air circulation, the shrinkage of unpackaged products increases. On the other hand, we are already accustomed to storing food in packaging, and the shelf life of food is generally short;
- slightly increased electricity consumption due to the additionally installed air cooler electric motor. The additional electric motor also introduces additional noise and vibration. Although, in reality, the increase in energy consumption and the increase in noise and vibration are practically not noticeable;
- the increased complexity and technical richness of refrigerators with the “No Frost” system leads to a slight decrease in their reliability.
Can summarize that the presence or absence of a “No Frost” system in a refrigerator is unlikely to serve as a decisive factor when choosing a refrigerator.




