Designed supply ventilation system for supplying air that has undergone preliminary preparation (cleaning, humidification or cooling, heating) to the room. It is placed either in one housing (monoblock supply unit), or is assembled from individual elements(coolers, air distributors, fans, valves, filters, air ducts and air heaters). Supply system ventilation is a ready-made unit for supply ventilation.
Select manufacturer:
|
Ostberg air handling units |
Air supply units Tion |
Compact supply ventilation systems are often used in cases where the level and quantity of pollutants released into the air reach the maximum permissible concentration level, and also require constant replacement of air, regardless of weather conditions. Supply ventilation is also used in clean zone rooms if it is necessary to protect them from the entry of cold air from the street or the penetration of contaminated air.
Types of supply ventilation systems
- Natural: allows you to supply the room with fresh air, but is less effective in cold seasons, as it drives frosty air inside the room and cools the room temperature. Air enters the room due to temperature changes outside and in the room itself.
- Forced: used in cottages and large houses. These air handling units turn on and off automatically as needed to save energy in cases where there is enough natural ventilation.
Types of supply ventilation systems
There are two types of heaters supply air: electric duct heaters (electric air supply units) and water duct heaters (duct air supply unit with a water heater). Electric duct heaters can be installed in any position (except for the position with the electrical panel at the bottom). For safe, proper operation of the heater, it is necessary to use an automation system that provides protection and comprehensive control.
Water duct heaters can be installed behind or in front of the fan. The heater is connected according to the counterflow principle. In order for air supply units with a water heater to function correctly, it is also necessary to use an automation system, which is somewhat more complicated when using water heaters.
Currently, there are many types of air supply units, but among the most popular are, first of all, air supply units with heat recovery and mini air handling unit. The air handling unit with recovery is designed for large rooms. It can retain up to 50% heat or cold. This function allows you to install coolers/heaters of lower power, which in turn saves gas or electricity.
Industrial air handling units are often installed in ventilation chambers or on the roofs of buildings. A supply air unit with cooling is installed in rooms for cooling products or materials. These can be workshops, refrigeration rooms in which it is necessary to maintain a low temperature. IN summer period Nowadays, household air handling units are also used in crowded places.
Unlike a supply and exhaust unit, an air supply unit with a recuperator works exclusively to draw in air from outside. This device It comes with both a water heater and cooling.
Today on the market of air supply units you can find the following options: ready-made systems, as a heated air supply unit, air supply gas installations, software configurable inflows. Therefore, pick up perfect option not difficult at all.
If you are interested in an air supply unit, the cost of which is affordable, you need to familiarize yourself with the catalog presented on the pages of our website. With us you can buy supply ventilation, air conditioner with forced ventilation quickly and economically. You can also compare prices for air handling units. Moscow, of course, offers the widest range, which is presented in our online store.
air supply units supply ventilation systems
If it is needed, supply ventilation systems
Different types of systems
Modern air supply units
supply ventilation systems
supply ventilation systems
Supply ventilation systems
Modern technologies of ventilation equipment make it possible to create high-tech systems capable of ensuring high-quality and safe gas exchange within a room or an entire building. Not the least important place in solving numerous ventilation problems is played by supply ventilation systems, which become the basis of all ventilation communications. Varied supply ventilation systems allow you to select optimal solutions for all types of buildings.
Design features of air supply units
Speaking about the supply exhaust ventilation in technology, as a rule, they mean systems of devices, equipment and instruments designed to replace indoor air. The designs of such systems consist of two channels, through one of which exhaust air is removed, and through the other, fresh air is supplied. Each channel consists of separate devices that are connected to each other by air ducts. Forced ventilation systems usually include elements such as:
- Fans that direct air movement through air ducts;
- Air intake grilles designed to protect air ducts from foreign objects entering them;
- Air filters that clean the outside air from impurities and small debris;
- Air valves that regulate the flow of incoming air and prevent cold air from entering the system when the system is turned off;
- Air ducts that connect all elements into one air distribution system;
- Air distributors that serve to distribute fresh air indoors;
- Automatic control systems for the operation of elements of the ventilation system, monitoring its main parameters;
- Silencers that reduce the noise level from the operation of fans in the system.
If it is needed, air supply units may contain additional elements, such as air heaters and coolers, humidifiers and dehumidifiers, throttle valves, recuperators, etc. Such devices allow not only the supply of fresh air to the room, but also make it possible to regulate its main parameters - humidity, temperature, etc.
Different types of systems
Modern supply ventilation systems And differ in their design - they can be monoblock or prefabricated type. The first type involves the installation of main components and elements in a single housing: fans, filters, air heaters, recuperator, automatic control of system operation. The second consists of separate devices interconnected by air ducts.
Design work when creating supply and exhaust ventilation systems, as a rule, begins with the preparation of a building plan, which indicates the area and purpose of each room separately. Based on this plan, a draft ventilation scheme for the premises is developed, which provides for all the required elements and their locations.
When starting to calculate system parameters, you need to determine its main indicators. All supply ventilation systems must perform certain functions, at the design stage it is necessary to identify all the structural features of future communications. These include:
- the air pressure in the system that the fans must create during operation;
- permissible noise level during system operation;
- cross-sectional area of the air duct channels and the speed of movement of the air flow in them;
- power of air heaters for air coming from outside;
- the magnitude of the performance of the ventilation system, which is capable of providing the necessary air exchange in various places of the building.
The supply and exhaust ventilation standards in force today provide for the necessary air exchange parameters, which depend on the area of the premises and the number of people in them. So, for residential premises the norm is about 2 -3 m 3 per hour per square meter or about 20 - 30 m 3 per adult. For household premises where there may be a high content of harmful impurities in the air, high humidity or unpleasant odors(kitchen, bathroom, etc.), the norm increases by 2 - 3 times. Select and design supply ventilation systems it is necessary with the help of professionals, since after installation of the equipment it will be difficult to adjust the operation of individual elements of the system.
During the day we pass about sixteen kilograms of air through our lungs. This figure significantly exceeds the amount of water drunk per day and food eaten. At the same time, we try to monitor the quality of food and avoid harmful additives, but sometimes we simply don’t think about the cleanliness of the air. But even in the case when the amount of impurities in the air does not exceed the maximum permissible values, from 15 to 100 milligrams of toxic substances enter the human body through the lungs per day: carbon monoxide, benzopyrene, formaldehyde, etc. In large cities, unfortunately, the situation with air pollution is very sad and the amount of harmful impurities in the atmosphere over the metropolis significantly exceeds the norm.
It doesn’t really matter whether you are on the street or at home. Modern apartment is something like a small chemical laboratory that constantly produces toxic substances. Almost all objects around you can be sources of pollution. Harmful substances are released during cooking and washing clothes. Furniture from particle board, synthetic carpets, linoleum, and laminate constantly emit formaldehyde and other toxic substances into the air. This is why it is so important to continuously refresh the indoor air with fresh, purified air from the street. A supply ventilation unit will help ensure such air exchange.
If you cannot ventilate the room because it is too noisy, dusty, cold or hot outside
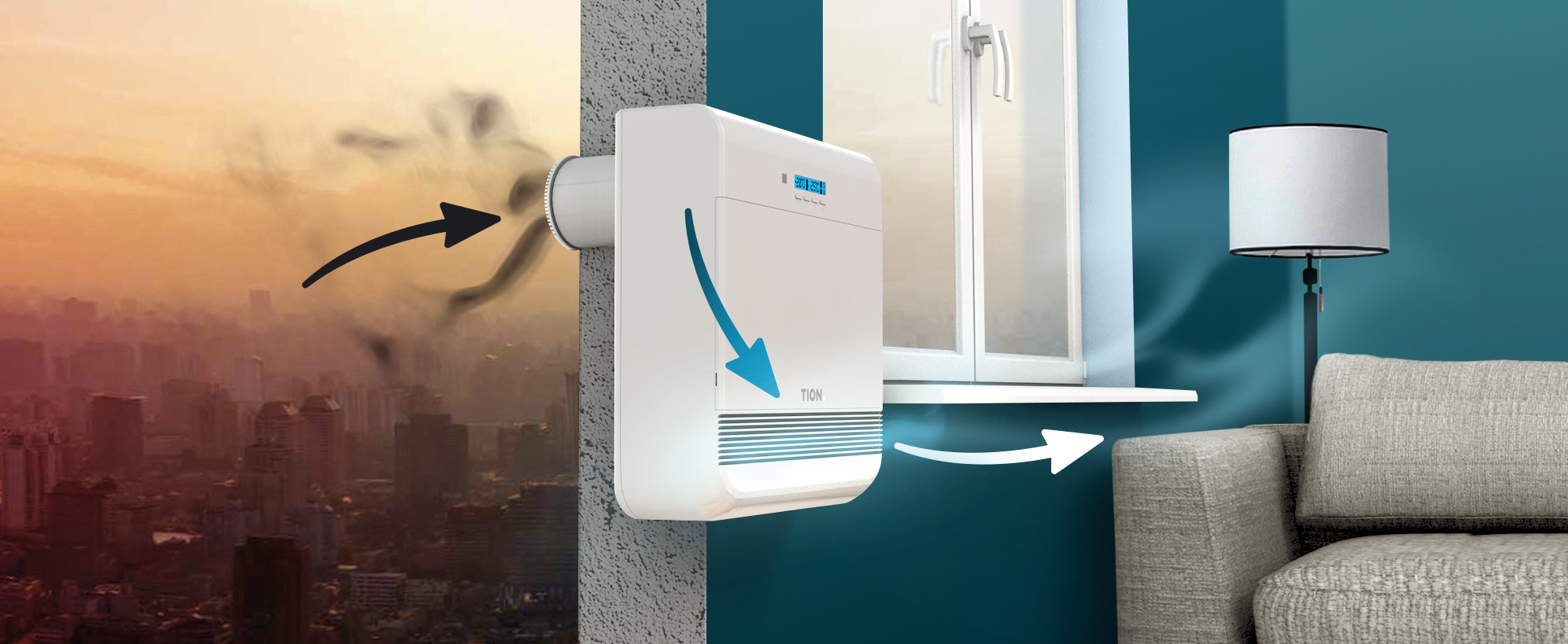

Studies have shown that toxic substances are released by synthetic materials much more intensely when exposed to solar radiation. If ventilation in apartments does not work well, and it is not possible to ventilate the room frequently, the concentration of harmful gases can reach a critical level. The sad consequence of this for apartment dwellers can be frequent headaches, respiratory diseases and even of cardio-vascular system. If you get rid of artificial materials, furnish the rooms with furniture from natural wood, you still can’t get rid of the danger. All building structures and soil continuously emit harmful substances, including extremely harmful radon - a colorless and odorless radioactive gas, which, in certain doses, is very dangerous for people.
If the humidity level in your apartment is too high
Properly selected and installed, it gives people comfort and health, great mood and performance. Unfortunately, many people believe that to achieve all these effects it is enough to install a regular air conditioner. However, air exchange in a house or in a separate room is a complex process that requires the installation of special equipment. To avoid confusion in concepts, you need to remember the following:
Air conditioner or split system, cools the air in the room. Supplying fresh air from the street is not part of its function; this task falls on a wall-mounted ventilator or supply unit. ventilation unit. Air conditioning can provide the desired coolness and comfort, and forced ventilation in the apartment (especially if there is plastic windows) is needed to maintain the required oxygen level.
Air purifier traps harmful impurities and purifies the air already circulating inside the apartment. Air supply units purify the air flow coming from the street, and therefore with their help you can achieve lower concentrations of toxic substances in the air that you and your children breathe.
Ionizer can improve the air quality in your apartment, but cannot provide oxygen flow. It is recommended to install the ionizer complete with an air handling unit. These devices work well together: the supply system supplies clean, fresh air into the room, and the ionizer improves the quality of this air.
Supply fan It is installed for ventilation of a room or apartment, but its functionality is limited to this. In the very best case scenario- it can clear the air of dust, but no more. Unlike a fan, air handling units can do a lot: heat air to the required temperature, clean it of toxic impurities, and supply it to the room completely silently.
Ventilation How to make an apartment comfortable
So, what affects our well-being in the apartment? Where does the feeling of discomfort come from and why, being in cozy room do we feel this way? Why do we still feel suffocated when sitting in a room with an open window or vent?
The concept of indoor comfort is quite arbitrary, but in our case, it consists of several components.
One of these components is clean fresh air, the continuous supply of which will be ensured by supply ventilation with a minimum noise level and which will not only purify the fresh air supplied from the street, but also maintain it optimal temperature. In the catalog of the company "Climate Control Engineering" you can find a wide selection of various compact air handling units, ventilators, energy-saving systems equipped with high-quality filters, carbon and photocatalytic (FKO filters), which allow you to get rid of not only fine dust, but also odors, harmful heavy connections and automobile exhausts. These air supply devices can be installed both in each individual room and in the entire apartment as a whole, and thanks to professional instrument and the high qualifications of our installation service, the installation of these air handling units can be carried out both during the renovation of an apartment, and in a residential, completely renovated clean room.
 |  |  |
|
 |  |  |  |
Why don’t we install supply valves like KIV, Aereko and others?
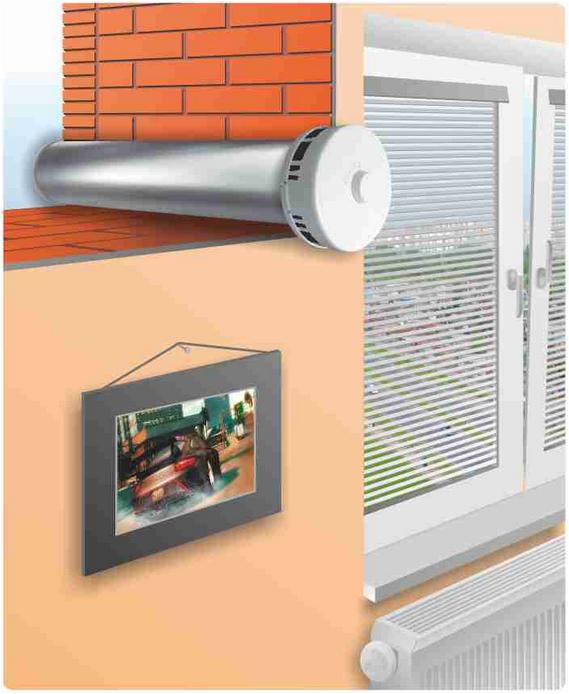 There are many reasons for this, but the most important is that with passive supply valves the ventilation process will only be carried out in the autumn. winter period. That is, in summer there will still be no air exchange. This is explained quite simply. Natural exhaust ventilation will work as long as there is a difference in air temperature indoors and outdoors. By creating a slight vacuum in the apartment, it promotes the flow of air from the street through the valves.
There are many reasons for this, but the most important is that with passive supply valves the ventilation process will only be carried out in the autumn. winter period. That is, in summer there will still be no air exchange. This is explained quite simply. Natural exhaust ventilation will work as long as there is a difference in air temperature indoors and outdoors. By creating a slight vacuum in the apartment, it promotes the flow of air from the street through the valves.
The greater the temperature difference, the better the ventilation will be. Accordingly, the smaller the difference, the weaker the hood works. As soon as the air temperature in the room becomes equal to the air temperature outside, the air exchange process will stop completely. Dampness will appear in the bathroom, a state of discomfort, suffocation will again arise and, of course, the hand will again reach for closed window. The question arises: why give money and bet supply valves, if in the summer you still have to open the windows?
Of course, if you live in nature and there is silence outside, fresh air, your neighbors don’t smoke, then you don’t need ventilators and air handling units and you can save money and install valves. In all other cases, for normal year-round ventilation in the room, it is necessary to install mechanical ventilators. Only a mechanical ventilator, by forcefully supplying air, creates a small overpressure indoors, and thereby “squeezes” air into the exhaust ducts located in the kitchen, bathroom and bathroom, normalizing the air exchange process. Since all air supply units and ventilators are designed for continuous, round-the-clock operation, the air exchange process in the room occurs all year round, including in the summer.
How to save on air heating in winter Air recuperators - economical ventilation
Perhaps everyone who thought about installing a ventilation system for their apartment was interested in how much it would cost and the cost of its installation. But, probably, an equally interesting question is how much year-round daily operation of this system will cost. Of course, operating costs will be minimal if you install ventilators that do not heat the air in winter, while consuming 30-50 W/hour all year round. Let's try, using the example of the heatless Aeropack ventilator, to calculate how much its round-the-clock operation will cost.
And so, we found out how much 24-hour operation would cost us. But for proper ventilation rooms, when the icy influx of fresh air does not cool the room in winter, ventilators and supply ventilation with air heating are used. Such devices allow you to ventilate the room more comfortably, but the power of these ventilators is much higher than that of non-heated ventilators, and therefore operating costs are higher. If we compare the energy consumption of such devices in the summer, as well as in spring and autumn, with non-heated ventilators, it will be approximately the same, because in the summer there is no need to heat the air, and electricity is consumed only to operate the ventilator fan. It’s another matter when winter comes and the air temperature outside drops to negative values. This is where the main costs of heating the air begin.
Cost of operating the air supply unit Selenga FKO
As a result of the calculations made, we can now imagine how much it will cost to operate a heated air handling unit. Of course, the ventilation in the apartment can be turned on and off periodically, but as practice shows, we spend more than 10 hours a day at home, so you can’t save a lot by turning them off. What then should you do if you don’t want to open the windows, but somehow need to ventilate the rooms? A way out of this situation may be installation. What is it, how does it work and why is it needed?
Why is fresh ventilation needed in an apartment?
Many people believe that installing fresh air ventilation is an unnecessary luxury. However, recent studies show that, unfortunately, this has already become a necessity. If earlier for the normal well-being of people it was enough to maintain an air replacement volume of about 30 m 3 per hour, then with the current state of the air environment in megalopolises and large cities, for a person to receive required quantity oxygen, you need at least 60 m 3 of fresh air per hour. This volume of air replacement can be achieved only by installing a forced supply and exhaust ventilation system in the apartment. And even in the case when the apartment is empty most of the time, it is necessary to constantly produce so-called background ventilation to remove toxic substances that are constantly emitted synthetic materials and building structures.
The Climate Control Engineering group of companies has been engaged in this for many years. Our specialists have excellent knowledge of the technology for installing air handling units and will help you resolve all problems associated with the ventilation process in your home.
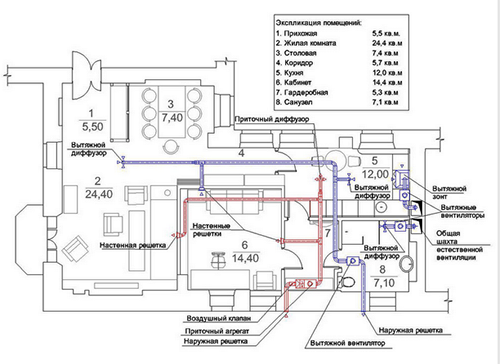
Supply ventilation systems are designed to supply air into the room. Fresh air is usually supplied after preliminary preparation which may include: heating, cleaning, cooling and hydration.
Classification of types of supply ventilation
Supply ventilation systems are classified according to a number of criteria:
ductless, in which fresh air enters the room directly through supply openings in the walls or windows of the building;
ducted, in which fresh air is supplied to the premises through an air duct system.
- According to the design of the ventilation network:
prefabricated, consisting of individual elements connected to each other by air ducts;
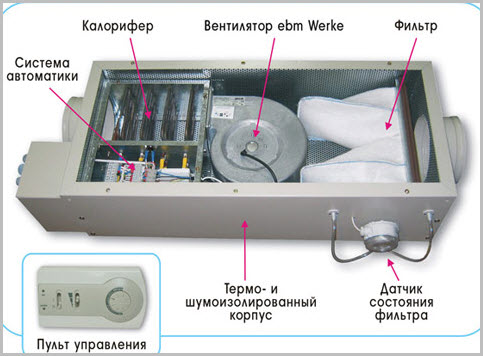
monoblock, which uses a supply ventilation unit that structurally combines several system elements in a separate housing (filter, heater, fan, air heater (grills, diffusers, etc.), cooler, valves, control system equipment, etc.).
- By ventilation method:
local ones, which supply a stream of fresh air to certain places in the room;
complex, providing complete and uniform air exchange in the room.
emergency (anti-smoke) systems, preventing the spread of smoke and facilitating the safe removal of people from the building in case of fire.
The productivity of air supply units can vary from several tens (mini-intake units) to several tens of thousands (central air supply units) cubic meters of air per hour.
The heating element (heater) provides winter time heating fresh air to the supply temperature to the room (from 18-20° to 27-29°C).
How does the supply ventilation system work?
A typical supply mechanical ventilation system consists of the following components:
- Air intake grille. Through it, outside air enters the ventilation system. These grilles, like other elements of the ventilation system, come in round or rectangular shapes. Air intake grilles not only perform decorative functions, but also protect the ventilation system from raindrops and foreign objects getting inside.


- Air valve. Serves to prevent outside air from entering the room when the ventilation system is turned off. An air valve is especially necessary in winter, since without it cold air and snow will enter the room uncontrollably. As a rule, air valves with an electric drive are installed in supply ventilation systems, which makes it possible to fully automate the control of the system: when the fan is turned on, the valve opens, when it is turned off, it closes.
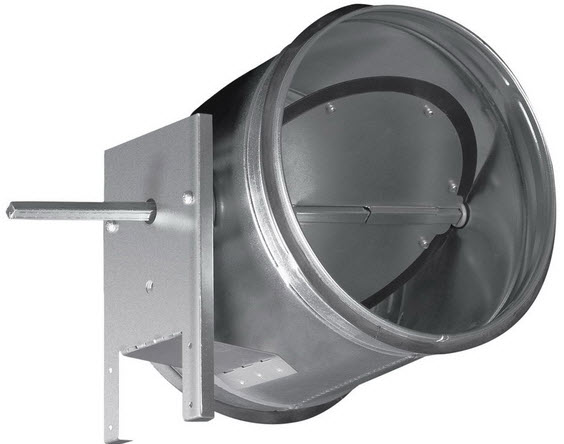



- Filter. This element is necessary to protect both the ventilation system itself and the ventilated premises from dust, fluff, and insects. Typically, the system is equipped with one coarse filter, which retains particles larger than 10 microns. If increased demands are placed on air cleanliness, then additional fine filters (for particles up to 1 micron) and extra fine filters (retain particles up to 0.1 microns) can be installed. The filter material in the coarse filter is a fabric made of synthetic fibers, such as acrylic. The filter must be periodically cleaned of dirt and dust, usually at least once a month.


- Air heater or air heater. Designed to heat air supplied from the street in winter. The heater can be water (temperature hot water must be at least 70°C) or electric. For small air handling units, it is more profitable to use electric heaters, since the installation of such a system requires lower costs. For large rooms (more than 100 m2 in area), it is advisable to use water heaters, otherwise energy costs will be very high. To significantly reduce the cost of heating cold air, a recuperator is used - a device in which cold supply air is heated by heat exchange with the removed warm air. The air flows do not mix.


- Silencer. Since the fan is a source of noise, a silencer must be installed nearby to prevent noise from spreading through the air ducts. The main source of noise during fan operation is turbulent air turbulence on its blades, that is, aerodynamic noise.

- Fan. Serves to supply fresh air to the room and create required pressure air flow in the network.



- Air ducts. After leaving the silencer, the treated air flow is ready for distribution throughout the premises.
For these purposes, an air supply network is used, consisting of air ducts and fittings (tees, bends, adapters). The main characteristics of air ducts are cross-sectional area, shape (round or rectangular) and rigidity (there are rigid, semi-flexible and flexible air ducts).
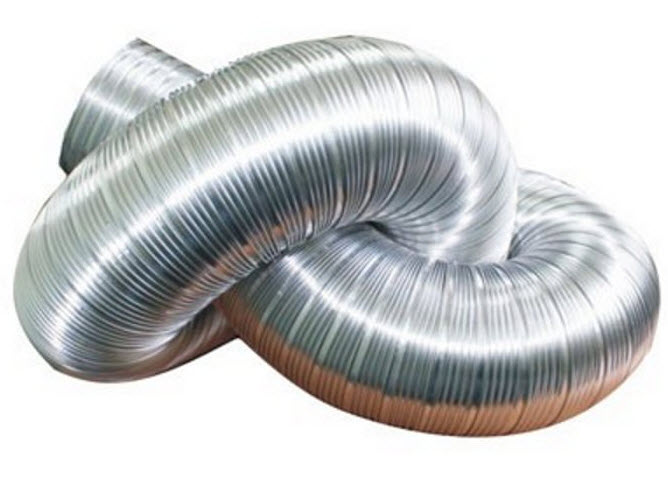



The flow rate in the duct should not exceed a certain value, otherwise the duct will become a source of noise. Therefore, the size of the air ducts is selected based on the calculated air exchange value and the maximum permissible air speed. Rigid air ducts are made of galvanized sheet and can have round or rectangular shape. Semi-flexible and flexible air ducts have a round shape and are made of multi-layer aluminum foil. The round shape of such air ducts is given by a frame made of twisted steel wire. This design is convenient in that the air ducts can be folded like an accordion during transportation and installation. The disadvantage of flexible air ducts is the high aerodynamic drag caused by uneven inner surface, therefore they are used only in areas of short length.
- Air distributors. Through air distributors, air from the air duct enters the room.
By design air distributors and air removal devices are very diverse:
- Air distribution grilles;
- Lampshades (diffusers);
- Perforated panels
- Slot air distribution devices;
- Nozzle air distributors, etc.





By geometric shape The jets supplied by air distribution devices can be:
- Compact jets are formed when air is released from cylindrical pipes, round and rectangular holes.
- Flat jets are formed when air flows out of slot channels air curtains, active distribution air ducts, rectangular elongated openings.
- Fan jets are formed when air is distributed through flat disk nozzles installed across the flow.
- Incomplete fan jets are formed when air is released through grates with blades diverging at a certain angle. Such a jet gradually transforms into a compact jet. Conical jets (a type of fan jet) are created when air is released through cone-shaped nozzles or lampshades in the form of diffusers in them with a flat reflective disk.
As a rule, grilles (round or rectangular, wall or ceiling) or diffusers (shades) are used as air distributors. Besides decorative functions air distributors serve to uniformly disperse the air flow throughout the room, as well as to individually regulate the air flow directed from the air distribution network to each room.
- Control and automation systems. The last element of the ventilation system is electrical shield, in which a ventilation control system is usually installed.
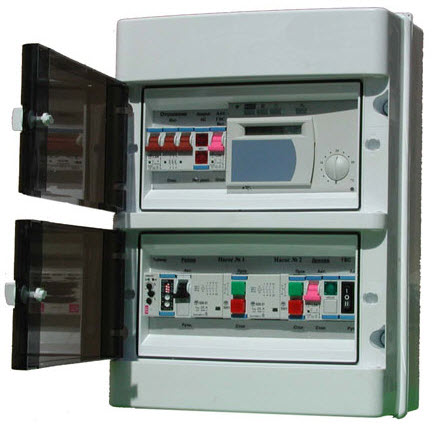



In the simplest case, the control system consists only of a switch with an indicator that allows you to turn the fan on and off. However, most often they use a control system with automatic elements, which turns on the heater when the supply air temperature drops, monitors the cleanliness of the filter, and controls air valve etc. Thermostats, hygrostats, pressure sensors, etc. are used as elements of the control system.
Supply system control
For ventilation of apartments and small offices today, small ventilation systems: a network of air ducts with an air supply unit. Operating modern equipment is convenient and simple. Using a remote control panel, you can adjust the air supply in five stages; in winter, you can smoothly adjust the temperature from 5 to 28°C. In addition, some devices have a timer that turns on the unit on a certain day of the week or time of day.

It is also possible to connect an external exhaust fan. Automation will ensure synchronous switching on and off of the supply and exhaust fans. In case of an accident, the control is equipped with a protection system. The unit is reliably protected from overheating. Built into the fan motor winding thermal protection. When triggered, it stops the fan, signaling with an emergency lamp. Heating elements The heaters are equipped with thermostats that protect against overheating and fire.
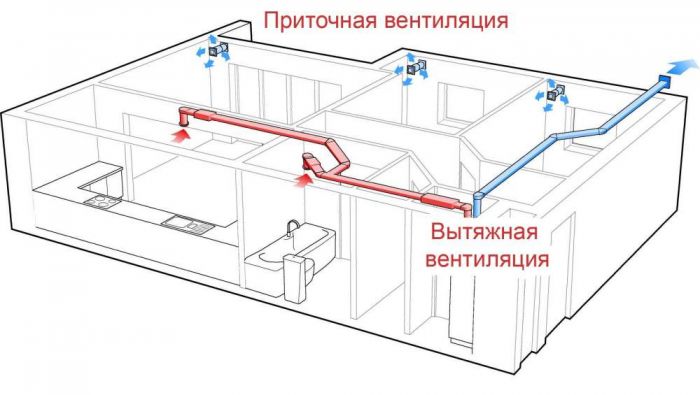
What is supply and exhaust ventilation?
A supply and exhaust ventilation system is a ventilation system that provides a flow of clean and fresh air into the room, and also removes harmful exhaust air from it. Both of these functions are performed simultaneously. As a rule, such ventilation is installed in country houses area over 100 sq.m.
Ventilation automation
Use supply and exhaust system ventilation with recovery in country houses is very profitable, since the cost of heating the house is sharply reduced, almost up to 90% (!). Indeed, thanks to the built-in heat exchange system (heat recovery), there is no need to heat the incoming air flow, as a result of which energy costs spent on heating the house, and with them your money, are significantly saved.
Air handling units are used in residential premises, industrial, public and administrative facilities.
In addition to air handling units, there are also air handling units - inflows . They differ from supply and exhaust units only in that they function exclusively to intake, process and supply air to the room. Air is removed using an independent ventilation system.
Main characteristics
- Air capacity (m³/hour)
- Heating power (kW).
- Pressure or external static pressure(kPa).
- Installation noise level (dB/A)
Scheme
Design
Air handling units are divided into systems for horizontal, vertical installation, as well as universal. Thanks to automatic control, you can smoothly or gradually change the performance of the installation, thermal power heater, and also set the timer to work in automatic mode.
Supply system-exhaust ventilation consists of the following elements:
- air valve - prevents outside air from entering the premises when the system is turned off
- air intake grille - air enters the system through it; it protects the installation from foreign objects and also has a decorative function
- filter - protection of the installation, as well as air filtration
- air heater (air heater) - heating supply air in winter
- fan - supplying air to the room and maintaining the required pressure in the air ducts
- air ducts - distribute air throughout the rooms
- air distributors - through them the prepared air after the air ducts enters directly into the room
- sound absorber - reduces the noise level from the installation
- heat and sound insulating panels - also reduce noise levels and increase efficiency
- automation and regulation system - allows for flexible effective management system
Equipment
- Supply and exhaust ventilation Systemair
- Supply and exhaust ventilation Ostberg
- Daikin ventilation units
- Supply and exhaust ventilation VTS
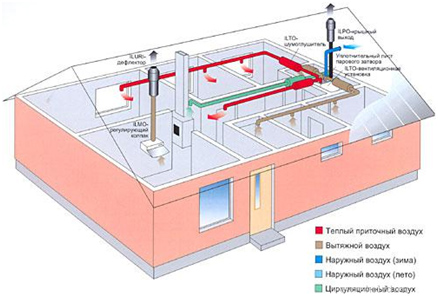
The principle of operation of supply and exhaust ventilation with recovery using the example of a country cottage
Every private house has a kitchen, bedroom, shower, toilet and hallway; ventilation must be installed in all these rooms to remove excess moisture from them, carbon dioxide, unpleasant odors and harmful emissions.
There are two air flows in the supply and exhaust ventilation system: inflow and outflow.
Inflow is the supply of fresh air from the street. The installation takes in fresh air, passes it through an air filter, cleans it, heats it using a recuperator and delivers it to the premises of the house.
Outflow is the intake and removal of exhaust air from the premises of the house. The installation collects moist, stale air from all rooms, passes it through a recovery system, where it takes the amount of heat necessary to heat the incoming air, and then discharges the cooled exhaust air outside.
Both air flows circulate in the system simultaneously, but they do not mix anywhere. They come as close as possible to each other only in the installation itself, where heat exchange occurs - hot exhaust air, leaving the house, gives 90% of its heat to the incoming flow. Thus, the need for standard (radiators, heated floors, etc.) heating of cold air is almost completely eliminated. In the traditional version, you heat radiators (warm floors), which heat the air; this is 90% more expensive than forced ventilation with a recuperator - count the money yourself.
Example: The temperature in the house is +27 "C, outside -13" C. Air from the house and from the street enters the installation where heat exchange occurs. After the heat recovery process, air from the street enters the premises heated to +25 "C, while the exhaust air is removed from the room cooled to -11" C. Energy consumption for the entire process is almost zero!
Saving energy on heating your home
In order to understand how energy is saved on heating a house, let's understand how the heating system as a whole works. Let's take as an example the radiator heating system of a private house with the most popular heating boiler of the Buderus brand. We set the temperature at + 21.5 "C on the control panel, the boiler begins to heat the water (coolant) and supplies it to the radiators throughout the house. The air in the room begins to heat up and reaches + 21.5 "C, after which the boiler turns off and again is activated when the temperature drops below + 21.5 "C.
Great, our heating system is working, the air in the room is warm. As soon as the room becomes warm, through cracks, walls, roof, open windows and doors warm air begins to leave, the room cools down. To maintain the set temperature, the boiler begins to work almost constantly and “devour” energy, and, accordingly, pull money out of your wallet by paying the gas (electricity) bill at the end of the month.
In order to avoid this, we install a supply and exhaust ventilation automation system with recovery in your home. The system begins to work, purify the incoming air, remove excess moisture, heat and harmful exhaust air. Thanks to the heat recovery system, the need for air heating drops to 60%. Accordingly, the boiler, which spent energy on constant heating of the house, reduces its work by 3 times, which saves up to 40% of your money on heating costs and saves heating equipment resources, incl. the heating boiler itself.
Below is a table of heating costs for a house of 170 sq.m., taking into account the cost of 1 kW of electricity = 3 rubles.
| Type of energy | Daily consumption | Heating season cost | Price internal system heating | Cost of boiler and equipment | Cost of connection to the main line |
| Main gas | 21 m 3 | RUB 15,284 | 400 thousand rubles | 50 - 100 thousand rubles | 100 - 750 thousand rubles |
| Electricity | 180 kW | RUB 160,620 | 200 - 500 thousand rubles | 50 thousand rubles | 100 - 750 thousand rubles |
| Diesel fuel | 22 kg | RUB 115,880 | 450 thousand rubles | 50 thousand rubles | No |
| Liquefied gas | 24 kg | RUB 118,440 | 500 thousand rubles | 350 thousand rubles | No |
| Heat pump | 40 kW | RUB 30,540 | 510 thousand rubles | 300 thousand rubles | 100 - 250 thousand rubles |
| Firewood | 48 kg | RUB 18,640 | 100 - 300 thousand rubles | 100 thousand rubles | No |
Ventilation
Types and classification of ventilation systems
Ventilation is intended to create an environment favorable to human health, and it must also meet the requirements technological process, equipment preservation and building structures, materials, products, etc.
Ventilation classification

Ventilation can be classified according to the following characteristic features:
- by the method of air movement: natural and artificial;
- by purpose: supply, exhaust and supply and exhaust;
- by service area: local and general;
- by design: ducted and ductless;
Types of ventilation
Natural and artificial
A natural ventilation system is created without the use of electrical equipment (fans, electric motors). It occurs due to natural factors - the difference in air temperature outside and indoors, changes in pressure.
An artificial or mechanical ventilation system is used where a natural one cannot cope. Mechanical systems use equipment and devices (fans, filters, air heaters, etc.) that move, purify and heat air. Artificial systems can remove or supply air to ventilated spaces regardless of environmental conditions.
Can be used in offices, cottages, apartments artificial system ventilation. It is also possible to use natural and mechanical ventilation simultaneously.
Supply, exhaust and supply and exhaust
Supply ventilation system; filters fresh air into the room, heats it if necessary (during the cold season) and supplies it to the air duct system for subsequent distribution throughout the premises. According to SNiP, residential and office premises must be able to be ventilated, because... they must provide adequate amounts of fresh air for human breathing.
The supply unit consists of a housing where a filter, water or electric heater, fan, automation system, and soundproofing material are mounted.
Exhaust ventilation is used to create a balance between the flow of air entering and leaving the room. It can be represented by: roof-mounted, autonomous axial, centrifugal; And duct fans, as well as exhaust ventilation units.
The supply and exhaust ventilation system combines supply and exhaust ventilation. Such ventilation of industrial, administrative, public and residential premises is effective from both a sanitary and hygienic and economic point of view. It allows you to significantly reduce costs by using heat recovery, which can be used to heat the supply air in special heat exchangers (recuperators). Similar installations are widely used in office premises, cinema and concert halls, hotels, residential premises, swimming pools, etc. Supply and exhaust ventilation has a high heat recovery efficiency (up to 70%); and provides at least a twofold reduction in operating costs for air heating due to heat recovery. Its advantages also include ease of installation and maintenance.
Local and general exchange
Local ventilation provides air supply to certain places (local supply ventilation) and removal of contaminated air only from places where harmful emissions are formed (local exhaust ventilation). In such cases, this ventilation is effective and inexpensive.
The use of two types of ventilation: in industrial buildings where there are various harmful emissions (heat, moisture, gases, vapors, dust, etc.) and their entry into the room occurs in different conditions. Also, local ventilation is used mainly in production, while in domestic conditions general ventilation is used. The exceptions are kitchen hoods: They represent local exhaust ventilation.
Duct and ductless ventilation
Duct ventilation has an extensive network of air ducts to move air. If there are no channels (air ducts), for example, when installing fans in the wall, in the ceiling, during natural ventilation, etc., then this is ductless ventilation.