Innovative sound-absorbing window glass and high-quality soundproofing materials significantly reduce the level of external noise in the premises. However, a significant portion of indoor noise can come from internal sources such as ventilation and air conditioning systems. The noises they make, namely the monotonous humming and howling of the air, although they do not irritate as much as the sounds of a disco in the next building, but gradually weaken nervous system, provoke insomnia and stress.
That is why insulation of air ducts is considered one of the primary tasks that must be thought through and completed at the design stage.
Causes of noise in ventilation
The main reason for ventilation noise is vibration caused by turbulent air flows in the pipes. It most often occurs due to errors in ventilation design and incorrect acoustic calculations.
Even before ventilation is installed, the designer must carefully study the layout of the house in order to find out in which rooms acoustic noise should be minimal and in which it is possible not to install insulation.
Already on the basis of this calculation, the optimal installation location is selected, all the nuances of the ventilation system are calculated: materials, dimensions of air ducts, branching features, location of elbows and barriers. The type of ventilation equipment, as well as the insulation method, is chosen last, when all other nuances have already been taken into account.
Noises in ventilation pipes different nature, depending on which the following types can be distinguished:
- noise from equipment operation: convectors, pumps. Transmitted directly with air flows, through hoods;
- Vibrating noise from water cooler and fan. Occurs due to improper installation and insufficient level of rigidity of the walls of air duct pipes;
- “turbulent” noises that appear when air flows pass branches, dampers, elbows and other points of turbulence.
Sound insulation of air ducts with special materials can reduce or even completely eliminate all of the above types of noise.
Mistakes when designing ventilation systems
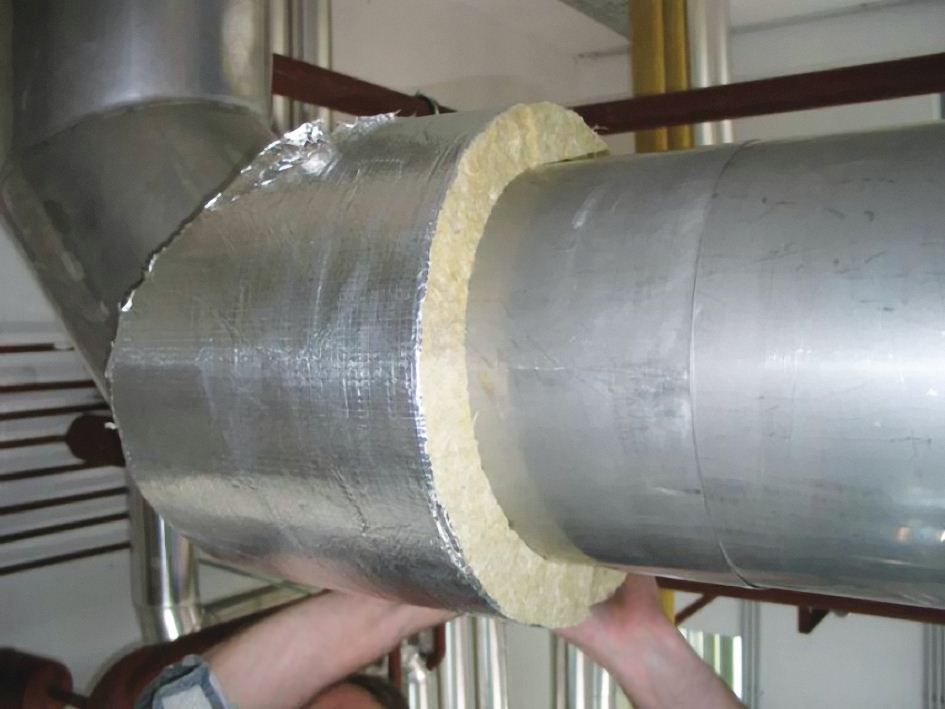

To the very common mistakes at the design stage, entailing an increase acoustic noise relate:
- irrational installation of noisy air ducts above rooms requiring low noise levels. Such noisy air ducts should be installed exclusively above workers and storage facilities, if it is impossible to change their location, and they will be located above living rooms, reception halls and bedrooms, then it is worth wrapping the pipes with insulating material and thickening their walls. In addition, in order to reduce noise due to turbulent air flows, it is worth installing oval or round air ducts;
- use of recirculation air systems without special air ducts. The air in such a system should be directed through the air duct, and not through the cavity of the false ceiling and ceilings. Otherwise, the noise from air freely circulating through this cavity will be simply unbearable for residents;
- lack of vibration isolation of the air duct. Vibration isolation measures include, first of all, the installation of vibrating elements that serve as a kind of counteraction to natural vibration in the system. In addition, it is worth remembering that all pipe connections adjacent to equipment elements must be flexible. Self-generated noise caused by turbulent air flows can be eliminated by installing large air ducts, through which the air flow slows down. Turbulent flows can occur in any area of ventilation, and the noise they create creates big problems for those who stay in a ventilated room for a long time.
Features of sound insulation of air ducts
The most popular method of sound insulation is laying special material inside or outside pipes (organic and fiberglass, rubber, polystyrene foam). In this case, the source of the noise is muffled, but the cause remains. As already mentioned, this problem should have been nipped in the bud, that is, at the design stage. All soundproofing methods are capable of reducing the noise level in a functional environment to one degree or another, however, none of them eliminates the root causes of noise.
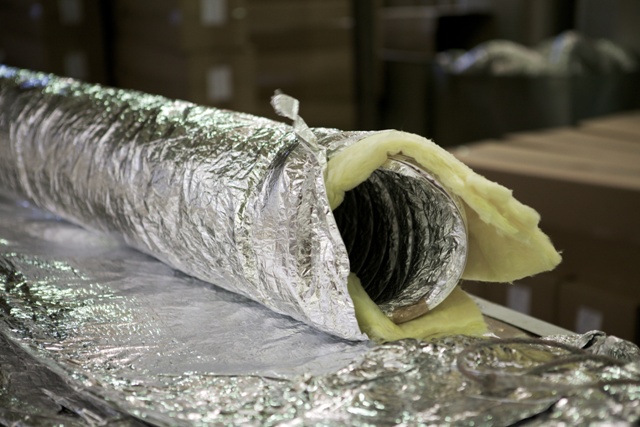
The best insulation properties are for materials with a fleecy coating: mineral wool, organic fiber. Not so long ago, such a material as lamella mats appeared on the construction market, notable for their transverse fibers. This material is good, first of all, because it does not form creases on the bends, so the material fits as tightly as possible to the pipe, and the noise level is reduced by as much as 8-15 dB (the final sound insulation value varies depending on the degree of noise).
In order to select the appropriate insulating material for a particular case, it is worth taking into account the cross-section and shape of the pipes. Obviously, the highest degree of insulation can only be achieved when the entire surface of the ventilation system is evenly covered with an insulator, which prevents the appearance of “sound breaks” (places where there is no insulating coating). All seams and joints must be carefully sealed with tape or tied with bandages.
To reduce the level of turbulent, uncontrollable noise, you can install a special absorption muffler.
Materials for insulation of ventilation air ducts
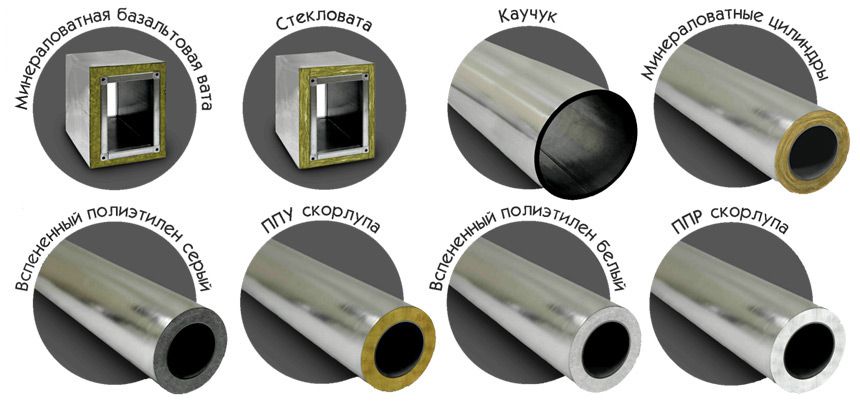
Thermal and sound insulation of air ducts is usually made using the following materials:
- mineral wool;
- extruded polystyrene foam;
- polyurethane foam insulation;
- foamed polyethylene.
The procedure for insulating air ducts with mineral wool includes the following steps:
- cleaning pipes from dirt;
- winding with one layer of mineral wool;
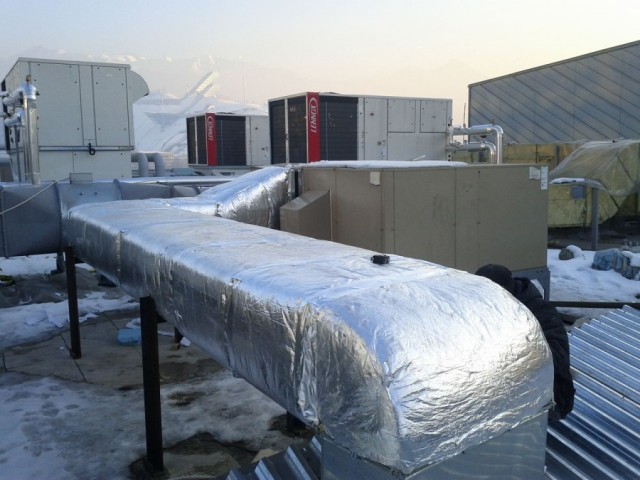
- an overlay of foil insulation 0.4 cm thick (so that heat does not escape outside and cold does not penetrate inside);
- sealing the seams with aluminum tape.
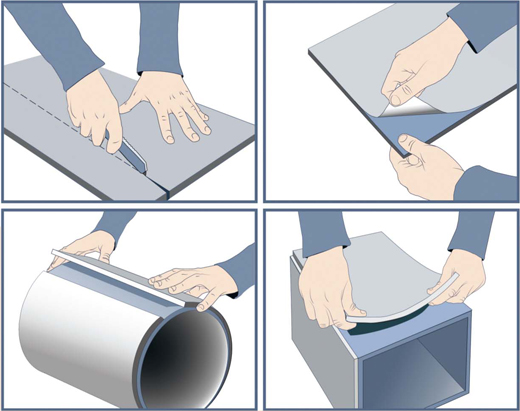
Sound insulation of air ducts with polystyrene foam insulation ensures the greatest durability of the pipes and increases their resistance to corrosion. For the insulation procedure, you need to cut polystyrene foam into pieces the right size using a knife, and put these half-cylinders on the pipe, shifting them by 20-25 cm, in order to shrink more tightly. The seams are sealed using special bandages.
Installing polyurethane foam and polypropylene foam is no different from installing extruded polystyrene foam. The only difference between these materials is that they do not burn and are less thermally conductive than expanded polystyrene and mineral wool.
The leading position in the frequency of installations in domestic conditions is occupied by such material as foamed polyethylene. The process of installing it is extremely simple: everything starts with measuring, then the polyethylene shell is opened along the seam and attached around the pipe, and upon completion of the work, the joints and seams are sealed with glue or tape.
The general rule for all types of ventilation insulation is that the material must be of high quality and the installation must be professional. Correctly selected material for insulation, and correct installation will save a significant amount on repairs ventilation systems, and will also reduce the risk of accidents.
Description:
Thermal insulation of air ducts performs the following main functions: Preventing the formation of condensation on both the internal and external surfaces of the air duct. Provide fire resistance to prevent the spread of fire in the event of fire. Reducing noise and vibrations that occur as air moves through the duct. Reducing heat transfer between the air flow in the duct and the external environment.
Thermal insulation of air ducts
Condensation formation, safety, noise, energy saving - these are the criteria that should be taken into account when choosing a material for thermal insulation of air ducts.
Thermal insulation of air ducts performs the following main functions:
Prevention of condensation formation on both the internal and external surfaces of the air duct.
Provide fire resistance to prevent the spread of fire in the event of fire.
Reducing noise and vibrations that occur as air moves through the duct.
Reducing heat transfer between the air flow in the duct and the external environment.
Condensation Formation
In ducts that carry cold air, the main problem is preventing condensation from forming on the outside of the duct.
The formation of condensation can lead to corrosion damage air ducts and mold formation. In addition, moisture can seep into the room, causing damage to the finish and furnishings. To prevent this phenomenon, it is necessary that the temperature of the outer surface of the air duct is not lower than the dew point temperature of the air in the room in which the air duct is laid. The problem can be solved by equipping the air duct with thermal insulation, which, along with low thermal conductivity, would have high resistance to vapor permeation.
The thickness of the thermal insulation layer is set taking into account the dew point temperature (which, in turn, depends on the temperature and humidity of the air in the room), the difference in air temperature in the air duct and in the room, the thermal conductivity of the insulation and the parameters of the air duct (shape, size).
Shown in Fig. 2 graph allows you to calculate the required thickness of the thermal insulation layer. In terms of moisture absorption, closed-cell thermal insulation materials have better performance.
It should be borne in mind that over time, a certain, albeit insignificant, moisture absorption occurs in any thermal insulation materials, which increases their thermal conductivity.
Materials with low vapor permeability should be protected with a suitable vapor barrier coating.
Thermal insulation and fire safety
The properties of a particular material in relation to fire safety determine its fire resistance. There are six fire resistance classes - from zero (non-flammable) to fifth - according to the degree of increase in fire hazard. The fire resistance class is assigned based on the results of tests during which a sample of the material is exposed to high temperatures.
For the organization of air ducts, materials with a zero (0) fire resistance class are used. If the channel has a multilayer lining, fire resistance class “zero-one” (0–1) is allowed. This condition is met if all surfaces in operating mode consist of non-flammable material thickness of at least 0.08 mm and provide continuous protection of the internal thermal insulation layer, which has a fire resistance class not higher than the first (1). Fastenings and connections, the length of which is no more than five times the diameter of the air duct itself, must be made of material with a fire resistance class of “zero” (0), “zero-one” (0–1), “one-zero” (1–0 ), "one-one" (1–1) or "one" (1). Air ducts of class “zero” (0) have external cladding from a material of fire resistance class not higher than first (1).
Noise
Air preparation and air distribution systems create noise that is transmitted, among other things, through the air duct system. Noise arises not only from the turbulence of the air flow passing through the air ducts, but also from fan operation, during which vibration and other acoustic effects are created. Air ducts can carry noise from room to room. You can combat noise by maintaining a low air speed in the air ducts, installing damping devices at the point where the fan is connected to the air duct, using elastic suspension for the air ducts, as well as damping gaskets where the air ducts intersect wall structures. Noise propagated through air ducts can also be attenuated by the use of special noise suppressors and soundproofing coatings. Many thermal insulation materials have good sound insulation properties and can be used as both heat and sound insulation. Thus, when choosing thermal insulation material For an air duct, its acoustic efficiency should also be taken into account.
Energy saving
The choice of the thickness of the thermal insulation layer for the purpose of energy saving is determined by economic considerations. Thermal insulation, by limiting the heat exchange between the air passing through the duct and the external environment, during the operation of the ventilation system allows for certain savings in energy resources. It should be borne in mind that thermal insulation has its own cost, which is subject to depreciation. Economic efficiency here is determined by the difference between the cost of energy resources saved per year and the amount of annual deductions for depreciation of the costs of installing thermal insulation. Both indicators increase with increasing thermal insulation thickness, but the growth pattern is different. Consequently, the greatest efficiency can be obtained only with a certain thickness of thermal insulation. This thickness varies depending on the type of insulating material and its cost. It should also be taken into account that it is not always possible to use the thickness that gives the greatest economic efficiency, as, for example, in the case of laying channels in suspended ceiling where space is extremely limited.
For the most popular materials used for thermal insulation of air ducts, the minimum permissible thickness, in accordance with current Italian standards regulatory documents, is given in table. 2. Type “A” air ducts include air ducts laid in an unheated space. Type “B” air ducts are channels built into external walls inside thermally insulated building structures(in this case, the minimum permissible thermal insulation thickness is reduced to 50%). Type “B” air ducts are channels laid in structures that do not communicate with either the outside environment or unheated rooms (the minimum permissible thermal insulation thickness is reduced to 30%).
Thermal insulation from inside or outside?
Thermal insulation of the air duct can be done from the inside or outside. In the first case, the air flow passing through the air duct is in direct contact with the thermal insulation. When using mineral wool or glass wool as thermal insulation, the surface fibers must be strengthened so that over time they do not peel off under the influence of air flow, especially if its speed is high enough. For such strengthening, adhesives are used that do not affect fire resistance. thermal insulation coating. However, these adhesives should not emit toxic gases in the event of fire.
When using thermal insulation inside an air duct, it is necessary to increase the cross-section of the air duct to maintain the design throughput at a given air speed. In addition, the side of the insulation that comes into contact with the air flow must be smooth enough so as not to increase resistance as air moves through the duct.
Today, the task of providing combined heat and sound insulation through insulating material is no longer as relevant as before, since often the noise problem is now solved by installing mufflers or soundproofing measures directly at the sound source. Because of this, the use external thermal insulation is currently preferred.
Another important circumstance associated with the refusal of internal thermal insulation is the prevention of the occurrence of pockets of bacteria, the formation of dust and dirt deposits, due to which the thermal insulation material can begin to delaminate, release volatile substances and lose its qualities.
In addition, with external thermal insulation, the risk of fire spreading from room to room in the event of a fire is significantly reduced.
Installation
Regardless of the location of the insulating material, most important factor– prevention of cold bridges that reduce the effectiveness of thermal insulation, as well as ensuring high vapor resistance (Fig. 3). Cold bridges can occur in places where ducts are attached to building structures.
Erosion of thermal insulation material is prevented by:
For internal thermal insulation - application composite materials, where thermal insulation is combined with a metal layer or film.
For external thermal insulation - use neoprene sheathing, galvanized steel sheet or aluminum sheet.
Characteristics of heat-insulating materials
Thermal conductivity coefficient l, W/m °C, is the most important characteristic of thermal insulation materials. Heat transfer resistance can be improved by increasing its thickness or choosing a material with a lower thermal conductivity coefficient. On the graph in Fig. Figure 1 shows the effect of temperature on the thermal conductivity coefficient of some thermal insulation materials.
Vapor permeability: Thermal insulation material can absorb condensation moisture. It should be taken into account that thermal conductivity increases with increasing moisture content. Fibrous and porous heat insulators with open pores are especially susceptible to moisture absorption. Such materials must be protected with appropriate vapor barrier coatings.
Acoustic Efficiency: Noise can be airborne, meaning sound waves travel through the air either as vibration generated by a fan or by vibrations of the air within an air duct. Sound waves are transmitted through the rigid structure of the duct network and building structure. Some of the sound energy is emitted in external environment, part is converted into heat due to the effect of internal damping of the material from which the channel is made. The degree of noise attenuation depends on the design of the channel.
Resistance to biological reagents: some materials may be exposed to mold, insects, microorganisms, leading to their destruction. The formation of a substrate of microorganisms is possible.
Maximum permissible operating temperature: determines the resistance range of the material used as thermal insulation. As a rule, this temperature range lies between –30 and +60 °C.
Sanitary and hygienic indicators: when using air ducts, toxic gases, as well as any other harmful substances dangerous to human life and health, should not be released.
Thermal insulation materials used
Mineral fibers. Mineral wool or glass wool insulation materials are supplied as molded rigid and semi-rigid (tube sections and panels) elements, or as a material whose density can be changed by pressing directly during installation, allowing it to be shaped to the desired shape. Felt is supplied in rolls. When installed externally, it is protected by a reinforced aluminum kraft sheet; when installed internally, it is protected by a layer of fiberglass with surface impregnation. Pipe sections are used for external lining of channels with reinforced aluminum protection.
Foam elastomers. Flexible closed cell foams. They are produced in plates or by extrusion followed by vulcanization of the foam. Outer side smooth, porous from the cut side. In terms of fire resistance, they belong to the category of self-extinguishing materials. Not susceptible to mold and microorganisms. They have a high degree of resistance to moisture absorption and vapor permeation.
Derivatives of hydrocarbon polymerization (polyurethane, polyethylene, polystyrene, polyisocyanate, polyvinyl chloride). Typically produced in plates, blocks, pipe sections, etc. These materials are either rigid thermoplastic (polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride), or rigid thermosetting (polyurethane, polyisocyanate), or flexible material (polyethylene, flexible polyurethane). Used for interior installation. Material with open pores has good sound insulation, but has the disadvantage of being susceptible to mold and microorganisms. Closed-cell materials, due to their lower porosity, are preferable from a sanitary and hygienic point of view, but have worse sound insulation. Closed-cell polyethylene foam comes in sheets and tubes and is fire-resistant and self-extinguishing. High flexibility makes it easy to give it the required shape. Polyurethane foam and polyisocyanate foam with closed or open pores are self-extinguishing or non-combustible materials. Supplied in blocks, which are cut into individual plates. Polyurethane is also supplied in the form of pipe sections, usually complete with a facing material (PVC, polyethylene or aluminum) used as a vapor barrier. Polystyrene is produced in the form of foam and extrudate, supplied in blocks that are cut into plates of the required thickness. With certain additives it is a non-flammable, self-extinguishing material. Closed-cell polyvinyl chloride has good moisture resistance and is classified as non-flammable.
Phenolic expanded resins. They have closed pores, are fire-resistant, and are not susceptible to microorganisms. Mainly used in refrigeration systems.
Reprinted with abbreviations from RCI magazine.
Translation from Italian by S. N. Bulekov.
- Thermal insulation: nuances
- Insulation against condensation
- Fireproof insulation of air ducts
- Sound insulation of air ducts: features
- Characteristics of some materials for air duct insulation
Modern air conditioning and climate control systems are necessarily equipped with an air duct. This device provides air supply and removal from the room. Air conditioning and ventilation systems are installed in a wide variety of rooms. This could be a warehouse, office, residential building, industrial complex, and so on. All this must be supplied with air ducts. The main goal of such systems is to maintain a given climate regime at minimum costs. This can only be achieved by insulating the air ducts.
A wide variety of materials can be used as insulation for outdoor or indoor air ducts. It all depends on what kind of protection is required this device. Air duct insulation is divided into thermal, fire, sound, and so on. All of these options are not always used. Sometimes one type of material, or sometimes a combination of them, can be used as insulation for air ducts.
Thermal insulation: nuances
Today, the most thermal insulation for air ducts can be used. various materials. Its main task is to prevent leakage warm air from the premises. For this purpose, protective barriers are most often installed at the system output.
This allows you to solve 2 main problems:

- When air flows through a long duct, it can cool down. Here, thermal insulation is used to keep these losses to a minimum.
- It is typical for such insulation for air ducts that it is also installed in those areas of the system where cold air masses move. Here it is imperative to protect them from warm air. This is especially true in cases where the flow is provided by natural circulation. It is very important to observe temperature differences here. This is exactly what thermal insulation does.
There are many materials that are used as duct insulation. This can be mineral wool, glass wool, foamed rubber, foamed polyethylene and so on. Most often, the choice falls on mineral mats, which are covered with a layer of aluminum foil. This material allows you to keep warm in any conditions.
Insulation of air ducts of this type is divided into internal and external. The first option is almost never used. The thickness of the material is selected depending on many factors. The main ones are temperature, humidity and aggressiveness. Only a professional designer can make the correct calculation. You can only get approximate results on your own.
Return to contents
Insulation against condensation

This type of insulation for air ducts is also very important. Cold air moves through the elements of this structure, the temperature of which is significantly lower than that present in the house itself. This leads to condensation forming on the walls of the air duct. If it forms in rooms where there is constantly high air humidity, then there is a high probability that it will fall out in the form of drops on the floor, ceiling and walls. Such an environment promotes the development of pathogenic bacteria and various diseases.
As insulation for air ducts, you need to use a material that will help equalize the temperatures of the two environments. It is very important to provide a high-quality surface layer here. It will act as a vapor barrier. Its main task is to prevent moisture from entering the insulation material. The base of this layer can be very diverse. Most often basalt fiber or polyethylene is used here. Option 2 is cheaper.
Foil insulation for air ducts must be taped at the joints with special tape. It will help protect against moisture penetration into the structure. When air duct insulation is implemented using rolled materials, it is imperative to use wire or tape for additional fixation.
Return to contents
Fireproof insulation of air ducts

All air ducts in the house connect individual rooms and help increase air circulation in them. In the event of a fire, fire can destroy them quite quickly. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to protect the devices using special fireproof materials. Most often, stitched mineral mats are used as insulation materials for air ducts. They completely prevent fire.
There are 2 main types of materials used - mineral mats and mineral slabs.
Plates can be used for air ducts that have square section. They are fixed using various pins and special washers. Mats can be used for rectangular structural elements of the system. They are connected to each other by wire. There may be a foil layer on top of them. It improves specifications material, and also allows you to significantly improve its appearance.
If the length of the air duct is large, then it is additionally necessary to attach fire insulation to the ceiling or other structural elements. It all depends on engineering solutions.
Sometimes situations arise that the distance between the air duct and the ceiling is significantly less than the thickness required for laying the insulating layer. In this case, it is allowed to exclude it from the top. When there is still a small distance, the material can be partially laid. Insulation for air ducts has the most varied nature and purpose, but when performing them, you must remember that everything is done in accordance with the design and relevant documentation.
Return to contents
Sound insulation of air ducts: features
When a powerful air conditioning system is running in a house, extraneous noise is sure to appear in it. Of course, you need to get rid of them. High-quality sound insulation has not yet interfered with any similar system. Most often, the source of extraneous noise is the blades of a running fan. There are others structural elements, which can bring discomfort into life from time to time. Sound insulation for air ducts is the only possible way out from the situation.
Some ducts are made of sound-absorbing material. He can eliminate many sounds himself. This tendency is observed if the air duct is made in the form of a special pocket and when it is made from certain types of polymer materials. All kinds of noise travel best through metal. However, most modern air ducts are made from this material. Here you cannot do without an additional layer of noise insulation. Sometimes it is enough to simply install duct mufflers. However, this measure is not always effective.
The best material that can be used is mineral wool. It has a fibrous structure and optimal density.
Noise reduction can also be achieved using other materials. For example, people actively use special boards that are made from fiberglass.
In buildings with large area and complex layout, ventilation and air conditioning is one of the main life support systems. However, the difference in the temperature of the air in the air ducts and in the room makes it very difficult to set the optimal temperature and humidity conditions.
Exhaust air ducts, which remove excess heat, significantly heat the room, and forced ventilation, through which cold air enters, is a source of condensation, which raises humidity. Thus, temperature and humidity indicators are very far from those recommended by regulatory documents.
To solve these problems, air ducts are insulated. The standard insulation material used for processing must perform the functions of thermal insulation, sound insulation and fire protection, in addition, moisture condensation must not be allowed either in the middle or on the outer shell.
Types of insulating materials
The most popular insulating materials that the market offers can be divided into several categories depending on the area of application and technical specifications which are put forward to them.
Calculation of thermal insulation
In order to prevent moisture condensation on the surface of the box, it must be thermally insulated. The thickness of the thermal insulation of air ducts can be calculated by knowing the following indicators:
- the expected difference in temperature inside the air duct and in the room through which it passes;
- dew point;
- thermal conductivity of insulating material;
- duct dimensions.
The formula for calculation depends on the diameter of the duct:
For systems with a pipe diameter greater than 2 m, the formula is as follows: 
For air ducts with a diameter of less than 2 m, the calculation formula is as follows: 
λ from is the thermal conductivity coefficient of the insulating material;
α n - heat transfer coefficient from the surface of a thermal insulating product;
t in - air temperature inside the duct;
t o - room temperature;
t p - temperature on the surface of the thermal insulating material;
d from - insulation thickness, δ from - insulation thickness.
dtr - pipe diameter.
The thickness of thermal insulation is directly proportional to its thermal conductivity and inversely proportional to the heat transfer rate of the surface.
Thus, we can conclude that the use of non-foil thermal insulation more effectively protects the air duct from condensation. In addition, such thermal insulation will be significantly thinner and cheaper, which will have a positive effect on the cost. The widespread use of insulating materials with an outer shell of foil is due solely to stereotypes and force of habit.
Installation of thermal insulation
 For small-diameter models, self-adhesive thermal insulation for air ducts is predominantly used. Despite high level To ensure adhesion of the adhesive to the metal, the seams are additionally taped with aluminum tape. And the material itself can be additionally secured with tape, metal or polymer clamps or metal wire.
For small-diameter models, self-adhesive thermal insulation for air ducts is predominantly used. Despite high level To ensure adhesion of the adhesive to the metal, the seams are additionally taped with aluminum tape. And the material itself can be additionally secured with tape, metal or polymer clamps or metal wire. 
The process of gluing mineral-based heat-insulating material without a special adhesive layer onto medium-sized air ducts also does not present any particular difficulties. 
- The surface of the air duct is pre-cleaned of dust and dirt. Fat stains that may interfere with adhesion are removed.
- The insulating material is cut according to the dimensions of the air duct;
- Glue is applied to the metal;
- Thermal insulation is applied to the coated surface;
- Rolled with rollers for better adhesion over the entire area;
- The seams are taped with aluminum tape.
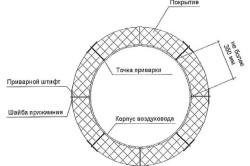
The process of installing insulation on large-section air ducts is much more labor-intensive. To do this, you need a resistance welding machine, with which pins are welded to the surface of the metal. 
There are ready-made pins with pressure caps and a metal base on which an adhesive polymer mixture is applied. Their installation does not require special equipment, but the cost of such devices is disproportionately higher. To install them, it is necessary to thoroughly degrease the surface at the gluing point. 
A heat-insulating mat is placed on the installed pins, which is blocked with pressure washers. The seams are taped without fail. Additional fastening with polymer or metal clamps is also performed.
Air ducts are important element the entire climate system of the building, which is installed in the form of branched channels through which air circulates. Proper thermal insulation of air ducts will help avoid the formation of condensation in the main line responsible for supplying clean air indoors, because here this probability is very high due to the collision of cold and warm atmospheric masses.
Purpose of insulation
Despite the name, duct insulation performs several tasks simultaneously, namely:
- prevents the formation of condensation;
- reduces vibration and reduces noise levels during operation;
- has a fire-fighting effect;
- significantly reduces heat losses.
Types of insulation
For insulation work on air ducts, any materials for this purpose that are used for walls, floors or ceilings can be used. However, there are separate samples specifically designed for this purpose.
Special heat insulator
For example, such a material is synthetic foam rubber, produced in the form of elastic flexible sheets. It holds its given shape perfectly, lasts for a quarter of a century, does not burn at all, and has soundproofing properties.
When exposed to moisture, rubber does not rot, and its thermal conductivity reaches 0.036 W/m C.
Traditional materials
TO traditional insulation can be attributed:

- mineral wool (0.035 – 0.045 W/mS, operation for at least 30 years);
- basalt fibers (0.030 – 0.048 W/mS, lasts about 50 years);
- glass wool (0.035 - 0.05 W/mS, without replacement up to 25 years);
- foamed polyethylene (0.04 W/mS, service life up to 80 years);
- polyurethane foam (0.02 - 0.03 W/mS).
In modern practice, insulated air valve, during installation of which thermal insulation for the air duct system is not required. This design consists of a frame, heating element and rotary vanes. With its help, the supply of heated air is regulated. To some extent, the valve is a kind of insulation.

As the air is drawn in, it heats up, and the line between cold and hot air masses disappears. Each individual ventilation system requires its own valve, but careful calculation will be necessary, without which it is impossible to select the correct device.
Material selection
Before calculating the thickness of the material, you need to familiarize yourself with the requirements for this type of product.
Thermal conductivity and vapor permeability
First of all, the material must have a low thermal conductivity coefficient. No less important parameter is also vapor permeability, on which the product’s ability to absorb moisture depends.

Fibrous and porous insulation must be additionally protected with a suitable coating.
Sound absorption
It is desirable that the insulation have a sound-absorbing effect, because the operation of climate channels is associated with air vibrations, which means that characteristic noise will appear. We must not forget about the impact of biological phenomena (mold, microorganisms, insects).
Temperature and environmental friendliness
The operating temperature at which the material will not lose its properties is limited to the range from –30 to +60 degrees, and it is necessary to exclude the release of toxic substances harmful to humans and animals.
Factors influencing the method of insulation
High-quality thermal insulation for the treatment of air ducts directly depends on the thickness of the material, external temperature, air humidity, climatic conditions in which the duct is constantly located and other factors.

There is a special table with combined indicators. You can familiarize yourself with the standards in SNiP 2.04.44-88. The installation method of the insulating material is selected taking into account the location of the flexible air duct (indoors or outdoors).
Street work
If the air duct was previously insulated, it is necessary to carry out preparatory procedures and remove the old layer of insulation from it. Then the surfaces are cleaned of glue and other remnants of previous compositions.
Sheet insulation
When using sheet or roll material immediately begin winding the channel with the selected insulation, ensuring required quantity layers, which depends on the insulation requirements.

The best solution for such manipulations would be a self-adhesive base.
Polyurethane
It is necessary to take into account that to install a polyurethane insulator, you will have to construct a reinforcing frame from a special mesh (metal or synthetic). The frame is stretched onto the flexible surface of the air duct, and its ends are fixed together with fastening bolts. Sometimes bolts are replaced with metal clamps.
Insulation mats
The most difficult task is laying insulating mats. Due to their large thickness, they are inconvenient to work with. As in the previous case, the material is fixed using metal tape clamps or flexible wire.
Waterproofing
Thermal insulation for covering air ducts must be protected by a layer that provides durable and reliable waterproofing that can be used for a long time.
![]()
The protection must be secured in such a way that it is not torn off by the wind or spoiled by other climatic phenomena. The role of such “armor” is most often a sheet of galvanized sheet or neoprene, which is gradually replacing the metal part from use.
Interior work
The technological process for insulating air ducts inside a building is identical to that used for external work. The only difference is that there is no negative factors in the form of climatic phenomena.
However, if highways are laid in places with high humidity, without additional protection it won't work out. As for private houses or apartments, there is no reason to worry about a negative environment, and the work will not be much different from treating walls or floors.

On initial stage thermal insulation for internal air ducts consists of installing a membrane that will provide waterproofing effect. Then you need to fix the insulation, on top of which another layer of membrane is fixed, or better yet, aluminum foil. Both of these materials will play an important role as a vapor barrier.
How to calculate the insulation layer?
It is very important to correctly calculate the thickness of the thermal insulation. We will need two main material parameters:
- Thermal conductivity index.
- Surface heat transfer index.
To make it easier to navigate, below is a table that shows the thermal conductivity of the most popular insulation materials.

When calculating the thickness of a material, we can say that the less it conducts heat, the thinner its layer can be, and vice versa.
There is an opinion that when treating an air duct it is preferable to use insulation that has a foil layer, but this is a misconception. Modern construction market offers a variety of insulation materials that, even without foil, are superior in their useful properties to the above-mentioned material.
For example, the same synthetic rubber copes well with its protective functions. Experts advise Special attention pay attention to ease of fixation, so self-adhesive insulation is better than others here.




