Nitrogen fertilizers are needed to feed garden and ornamental crops. With their help, plants begin to grow intensively and acquire large, richly colored leaves. This article is all about the use of urea, which improves the growth of green spaces in the city and rural greenhouses. Practically get to know proper feeding plants with urea, you can watch the video.
Urea - how to apply fertilizer correctly
A large compost pile insulates itself and retains the heat of microbial activity. Its center will be warmer than its edges. Piles measuring less than three feet cube have problems with this heat in the winter, while piles larger than five feet cube do not allow enough air to reach the germs in the center. These proportions have important, if your goal is fast, high-temperature composting. Large piles are useful for composting diseased plants or trees because high temperatures will kill pathogens and insects.
![]()
Urea: from what and for what?
The first of the synthesized protein compounds is urea. This scientific name is urea - a fertilizer for feeding garden and ornamental crops, which is used to accelerate growth. Urea belongs to the group of nitrogen fertilizers and is used in agriculture since the 18th century.
All life on Earth, including compost microbes, requires a certain amount of water and air to sustain itself. Microbes function best when the compost pile has plenty of air passages and is about as wet as a chopped sponge. Extremes of sun or rain can adversely affect this moisture balance. As a general rule, the moisture content of compost should be between 50 and 60% based on the total weight. Wet piles that leach water do not contain oxygen and can ferment and cause odor problems.
Pros and cons of feeding plants with urea
Never cover compost piles with plastic because this prevents air entry. Cured composts can be covered, but this can also cause problems. Compost blankets allow air exchange but shed rainwater from piles.
The product is produced by synthesis from inorganic substances and is a granular mass consisting of round, milky, sometimes translucent granules. Currently, the industrial production of urea is in the form of tablets.
Urea can be purchased in granule form
In terms of its chemical composition, almost half of urea consists of pure nitrogen, which dissolves without residue in any liquid, including water.
How to prepare and use compost
The larger the pile, the higher the temperature and the faster composting occurs, but only up to a certain point. This can be a problem in dry composts, especially in summer. Remove grass and turf from the area where you are building your compost pile to ensure the materials come into direct contact with soil microorganisms. For getting best results The following "recipe" for creating a compost pile is recommended.
1st layer: 3-4 shredded brush or other coarse material on top of the soil surface. This material allows air to circulate around the base of the pile. 2nd layer: 6-8 mixed waste, leaves, grass clippings, etc. materials should be “sponge”. 3rd layer: 1 soil serves as a modifier by adding microorganisms to the pile. 4th layer: 2-3 manure to provide nitrogen needed by microorganisms. Add one pound of urea fertilizer or 10 pounds of composted poultry manure for every yard of leaves or brush if organic sources of nitrogen are not available. Generally, manure should not be used in cities to reduce the likelihood of fly problems. Level 5: Repeat steps 1-4 until the bit is filled. Roll out the "pool" at the top to catch rainwater in summer conditions.
- Add water if the manure is dry.
- Soak these high carbon materials in water before composting.
When applied to the soil, granulated urea gradually dissolves in the water that the plants receive when watering. Slowly entering the plants, dissolved urea nourishes the roots for a long time, gradually, throughout the entire period of growing the crop. In the soil, nitrogen changes its chemical composition, from the amide form to the ammonia form, and then to the nitrate form. Slow change chemical composition guarantees prolonged nutrition of plants with substances necessary for growth.
At this time, you will notice that the pile is “settling.” This is a good sign that your heap is working correctly. After 3-4 weeks, the materials are unrolled into a new pile, turning the outer part of the old pile into the center of the new pile. It is best to turn the compost a second or third time. The compote should be ready for use within three to four months. A pile started in late spring may be ready for use in the fall. Start a new pile in the fall for use in the spring.
You can compost even faster by turning the pile more often. Check the internal temperature regularly; when it has reduced significantly, rotate the pile. The compost is ready to use when it is dark brown, crumbly and earthy-smelling. Compost usually needs to be at least 4-6 months old for use with plant seedlings. Leave it on the surface or work it onto the surface of 1-2 soils for most applications. It is best to keep organic matter close to the soil surface. This is known as mulching gardening.
Nitrogen starvation manifests itself in plants in slower growth, yellowing of leaves, inhibition of plant development and complete death. The introduction of urea during the formation of fruit trees And berry bushes unnaturally thin and short branches with small discolored leaves. Nitrogen deficiency is expressed at the beginning of leaf fall in summer period when most of the leaves on the plants turn more yellow early date than it should be in nature. In spring, weak, underdeveloped buds form on plants lacking nitrogen.
It is much easier to control weeds in gardens that are mulched with compost between rows of plants. The compost used here also does not need to be as decomposed as the one working in the seeds. Table 2 is a guide to more efficient composting. Quick Guide composting at home effectively.
Finding the best companion for you
Tree clippings, leaves and grass clippings can be used as mulch to control weeds and retain water by simply spreading them under the plants. Tree services, if they are in your area, will often supply wood chips for free. Chips can also be used for informal garden paths. Adding one pound of urea or 10 pounds of composted bird droppings per cubic yard of shredded wood with plenty of water speeds up the process.
It is allowed to feed fruit trees and shrubs with urea; it is an effective fertilizer for strawberries, strawberries, etc. vegetable crops, including cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, carrots, etc.
Urea - how to apply fertilizer correctly
When fertilizing with nitrogen fertilizers, in particular urea, several types of plant nutrition should be distinguished:
No Bag - Lawn Maintenance Plan
A "Don't Forget It" lawn care plan can save homeowners time, energy, fertilizers, pesticides and money, while also reducing the amount of waste sent to our landfills. The principle is simple: return the clippings to the lawn. Leaving clippings on your lawn and allowing them to return to the soil will improve soil health and reduce the use of pesticides and fertilizers.
In fact, grass clippings contain valuable nutrients that can generate up to 25 percent of your lawn's fertilization needs. One hundred pounds of grass clippings can generate and recycle as much as three to four pounds of nitrogen, one-half to one pound of phosphorus, and two to three pounds of potassium back into the lawn. These are the three most important nutrients needed by lawns and are commonly found in lawn fertilizers.
Pre-sowing treatment– urea granules are applied into the furrows during spring plowing. The depth of incorporation of urea into the soil is at least 4 cm.
Fertilizer application
Fertilizing with urea during sowing events – the best option is the use of the composition in combination with potash fertilizers. In this case, it is not allowed for the granules to be mixed with the seeds; it is necessary to provide a layer of soil between the granulated fertilizers and the seed.
Why then do many homeowners cut their grass? Basically, it is a personal preference and habit that most homeowners have acquired. This way you can learn how to make compost easily and in turn help protect environment, save money and improve your soil at the same time. Good luck learning how to compost at home.
Gardening in the Mediterranean country seems to go hand in hand with growing olive trees - from planting a new grove to tackling a forgotten tree or two. Photos by Davina Michaelides unless otherwise noted. In "Olive Grove" - "Diary" by Brian Chatterton.
Fertilizer application during the period of growth– most effective method is foliar feeding landing To do this, urea is dissolved in water, spraying on the green mass is carried out in the early morning hours or at sunset, in calm weather.
Important! Foliar fertilizing with urea is not recommended on days when precipitation occurs.
Cardamyl in autumn and spring. From time to time, some of them have been killed in the name of rejuvenation, and the general condition is poor. Yields vary and currently average around 10kg per tree, which if you know your olives you will know is pathetic.
A huge threat to olive crops is the ubiquitous olive fly, a priority has been to initiate a management program that will deal with this minute but extremely threatening pest. To control the olive fly we decided to use a Spanish olive fly trap. This consists of a clear plastic 5 liter bottle which has 5mm holes drilled around the top. These holes are designed to trap flies. The bottle is then filled with 1 liter of ammonium bicarbonate solution, the cap is screwed back on, and each tree receives a trap.
An aqueous solution of urea does not burn the leaves; it is convenient to spray plants using special pumps. The usual norm for diluting a solution is from 9 to 15 g of urea per 10 liters of water, and it matters which plants are planned to be treated - herbaceous plants spray with a more gentle composition, trees and shrubs with a concentrated one. Adult apple and pear trees need feeding in a ratio of 200 g of dry urea per bucket of water. For cherries, plums and apricots, the urea consumption will be 120 g/bucket.
Urea: from what and for what?
We hang them using plastic steel wire hooked onto a convenient branch in the shade. Flies simply love the delicious aroma of the solution inside the bottles and fly from miles around in search of the source. Inside the bottle they cannot find their way out, because all the attractant odors are inside.
As far as results are concerned, this is a controversial issue. I wonder if this was due to the success of the fly traps or the lack of pesticides that allowed the olive fly predator population to breed and prey on them. The point is that while our traps caught a lot of olive flies, they also caught many other insects, some unidentified, but the total numbers were lower than we expected.
Important! One tbsp. a spoon holds 10 g of urea; matchboxes - 13 g; faceted glass - 130 g of urea.
Treatment with urea against pests
Spraying with urea is effective in controlling plant pests. Spraying is carried out in the spring, when a constant average daily temperature is +5 C. It is important to carry out the procedure before the buds awaken, then all pests overwintering in the scales and under the bark will be guaranteed to be destroyed.
When the fly question is more or less controlled, the next important factor for olives is water. The critical problem for our trees is that the last rain falls before the flowers open, and the first rain in the fall is usually after harvest. Local residents tell us categorically that olives should not be watered. However, the truth is that although olive trees can survive drought, they love to drink again and again. It takes 6 weeks with 4 ladies working 6 days a week and we give approximately 100 liters of water per tree though big trees get more.
A urea solution for pest control is prepared in a concentration of 50 to 70 g per 1 liter of water. Spraying with urea helps destroy aphids, weevils, copperheads and a host of other pests.
Treatment of the garden with nitrogen can be carried out both in autumn and spring.
In autumn, during the first stage of leaf fall, it is useful to spray trees with urea solution on which traces have been noticed. infectious diseases: scab, all types of spotting, rust and others. The solution is used to treat trees along the crown and leaf litter. This treatment is a very effective remedy for infectious diseases. garden trees, the garden next year will not be affected by infections. Simultaneously with the treatment, the urea solution fertilizes the plants.
In other words, 600 tons of water. The critical factor associated with watering in May is that if trees are irrigated under conditions fruit crops, this encourages them to “install” more fruit on the tree. Once again, timing is important: too early and the water is wasted; too late and the oil content decreases. With so many trees and such a long period that each operation requires, some trees are watered too early and some quite late - but the overall effect is to increase the overall fruit tonnage, which is beneficial.
Pros and cons of feeding plants with urea
The positive properties of urea are:
- When fertilized with urea, plants easily absorb nitrogen, which has a positive effect on their growth and the expansion of green mass.
- Treatment of plants with a solution of fertilizer on the leaves does not cause burns to the leaf blade; this foliar feeding is an effective and gentle means, which, along with fertilizing plants, can effectively fight garden pests, as well as pathogenic infections.
- The urea solution is quickly absorbed by plants sensitive to elevated pH levels in the soil.
- Excellent results were noted when fertilizing plants with urea in irrigated areas, as well as when applied to crops grown when the beds were filled with water.
It is very important to observe the dosage when applying fertilizers.
This year, only the “runaways” were destroyed - two or three branches per tree. These are the branches that rise vertically up and out of a gently sloping tree. They are too tall and difficult to select, and removing them allows more light to penetrate into the body of the tree. The end result of this first phase of the program is a reduction total height canopies, which will greatly facilitate collection. Second phase next year will drain the tufts of new growth, highlighting a few strong leaders for the future. During the third year it will grow again, which will be reduced, and so on until we reach happy and contented, comfortable shapes and sizes of olive trees.
- Guaranteed increase in yield in the garden or garden when feeding plants with urea.
- Ease and simplicity of foliar treatment of plants and the introduction of urea into the soil.
- Availability of fertilizer at price and availability.
The disadvantages of fertilizing with urea are the following aspects:
- A strong concentration of fertilizer when applied to the soil when sowing seeds can reduce the germination of seeds and delay their germination.
- Urea requires careful storage.
- The use of urea in a mixture with phosphorus fertilizers is possible only when mixing absolutely dry substances; increased acidity from the effects of mixed fertilizing must be neutralized by adding chalk to the soil.
Advice! Granular urea must be stored in a dry place, otherwise the fertilizer strongly absorbs moisture and turns into lumps.
In terms of climate, in Çanakkale we are the frontier for olive production. Once every 100 years the temperature reaches minus 12 degrees Celsius. Every 50 years or so, statistically, temperatures reach minus 6, and temperatures between zero and minus 4 are expected typically every two or three years. We cleared the stumps to plant apples and others fruit trees. Some trees have lost the ends of their branches. We didn't lose a single tree - twelve 20 ton truckloads of bark mulch, and any other mulching materials that could be found were spread around as much as possible. more trees like thick mulch.
The size of the harvest depends on each gardener. Timely and competent application of fertilizing can ensure soil fertility and full return of garden and vegetable crops to the nutrients received on time.
Spraying the garden with urea: video
So that your garden looks well-groomed, the bushes are beautiful, the fruit trees are healthy and give good harvest, it must be properly prepared for the season. One of these important activities, in addition to whitewashing and pruning trees, is their spraying, and the most effective means Urea (urea) is considered for this purpose. Treating trees with urea solves several problems at once.
Urea refers to nitrogen fertilizers the highest concentration is almost 46%. Some novice gardeners confuse it with saltpeter, which can be dangerous to tree foliage. Urea is produced in the form of granular crystals of white and yellowish shades, which have absolutely no bad smell, easily dissolves in water (in hot water up to +80°C the process occurs faster) and is perfectly distributed over the treated areas. Due to its hygroscopicity, it should be stored in airtight containers. Gardeners value urea not only for its high nitrogen content, but also for high speed digestibility by plants. This is especially effective in combating harmful insects when every minute counts.
When working with urea, keep the following in mind:
- Urea refers to organic compounds, but is considered a mineral nitrogen-containing fertilizer.
- The effect of urea begins immediately and has a long period.
- Urea for gardening as a fertilizer is applied directly to the soil, since it has the properties of weathering.
- It is used in any soil, including in protected conditions (in greenhouses and hotbeds).
- Shows good efficiency on waterlogged soils.
- In soils with high biological activity, urea loses less nitrogen, which cannot be said about alkaline and neutral soils.
- Once in the soil, urea is converted into ammonium carbonate (ammonium carbonate).
- It is the most effective and safe nitrogenous fertilizer for garden plants in summer - does not burn foliage even with the wrong dosage.
- Another very useful properties urea is that it slows down the growing season - trees begin to flower later, and this helps to avoid the death of ovaries from spring frosts. This is especially effective for early ripening varieties of peaches, plums, and apricots.
- During the period when buds are forming on the trees, treatment with urea solves the problem with many pests and various diseases.
- Spring treatment of the garden with urea helps protect trees from frost.
- Urea is useless when dealing with old stumps; it is not capable of destroying them completely, but will only contribute to rotting.
- Under no circumstances mix urea with other fertilizers and minerals - chalk, simple superphosphates, lime.
Preparing the garden for processing
Before you start spraying your garden with urea in the spring, you need to consider some recommendations:
Treatment of the garden in the spring against diseases and pests with urea is carried out as follows:

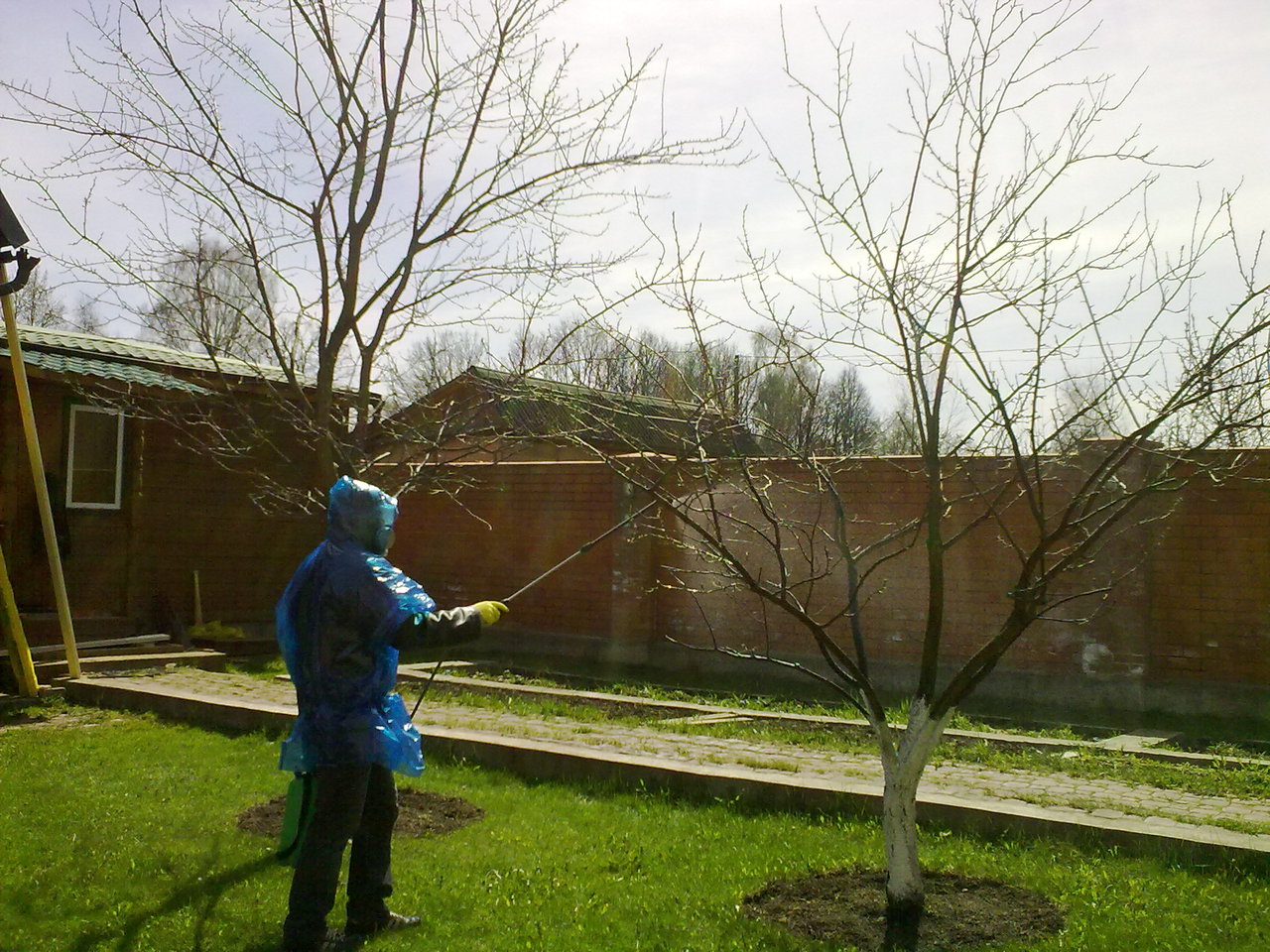
Processing of fruit trees
- You can begin treating your garden with urea if you have properly prepared the trees for this - you have dug up the ground underneath them, removed frozen and damaged branches, and whitened the tree trunks.
- A sunny and, most importantly, windless day is suitable for work. If the weather is hot, it is advisable to spray in the early morning or evening after sunset.
- It is necessary to prepare the solution and carry out the spraying itself in protective clothing, a mask, goggles and gloves.
- Urea will be especially effective in the fight against insects in combination with copper sulfate– 700 g of urea, 50 g of copper sulfate and 10 liters of water. This composition solves two problems at once - it destroys pests and fertilizes the soil.
- For spraying it is best to use a special sprayer. With its help you can process even very tall trees.
- When treating trees, do not skimp on the solution; it cannot be harmed.
- The second treatment of the garden can be carried out already during the flowering period of the trees, and the third immediately after the flowers have set.
- If precipitation occurs after spraying, it will be necessary to repeat the procedure, otherwise everything will be in vain.
- Root feeding of fruit trees during the fruiting period is carried out in the ratio: cherry and plum trees you will need from 120 to 150 g per 10 liters of water; apple trees will require 230-250 g per 10 liters of water.
- You don’t have to prepare a solution, but add dry urea, but in this case you need to thoroughly water the trees.
- In the case of feeding trees with organic matter, the rate of urea application must be reduced by 1/3 or half, this depends on the amount of organic fertilizer.

Processing other plants and shrubs
Surely many gardeners grow in their garden not only fruit trees, but also other plants, shrubs, both fruit and ornamental. They are also treated and fed with urea, which is used both as a fertilizer and as a means of combating diseases and pests.
- Active feeding of plants is carried out in case of nitrogen starvation, which manifests itself as follows:
- the plant begins to lag behind in growth;
- the leaves turn yellow and curl into a tube;
- flowering is weak, without ovaries;
- fruits and berries appear in small quantities and quickly fall off.
- For work, it is preferable to work in the morning or evening. No work is carried out during periods of precipitation.
- To prepare the solution, you need 30-40 g of urea per 10 liters of water.
Standards for root feeding:
- for cabbage and onions of any kind, beets, tomatoes, sweet peppers and potatoes, take 20-25 g per square meter. m.;
- for legumes and cucumbers – 5-8 g per sq. m.;
- for feeding strawberries, blackberries, strawberries and vegetables such as cabbage, cucumber or tomato - 20-30 g per 10 liters of water. For each bush or plant, 1 liter of solution is needed;
- gooseberries are fed in a ratio of 10 g per 10 liters of water;
- for currants take 20 g per 10 liters of water;
- squash, eggplants and zucchini require 10-12 g per sq. m.
Today, urea is the most popular means for feeding trees, shrubs and other plants - approximately 35% of all nitrogen-containing fertilizers. It can be safely called one of the most effective and safe, which is confirmed by the high and constantly growing demand. The cost of urea is slightly higher than that of other nitrogen-containing fertilizers due to the fact that it is not natural, but is obtained as a result of synthesis from ammonia and carbon dioxide. But in in this case We can safely say that the price justifies the quality.